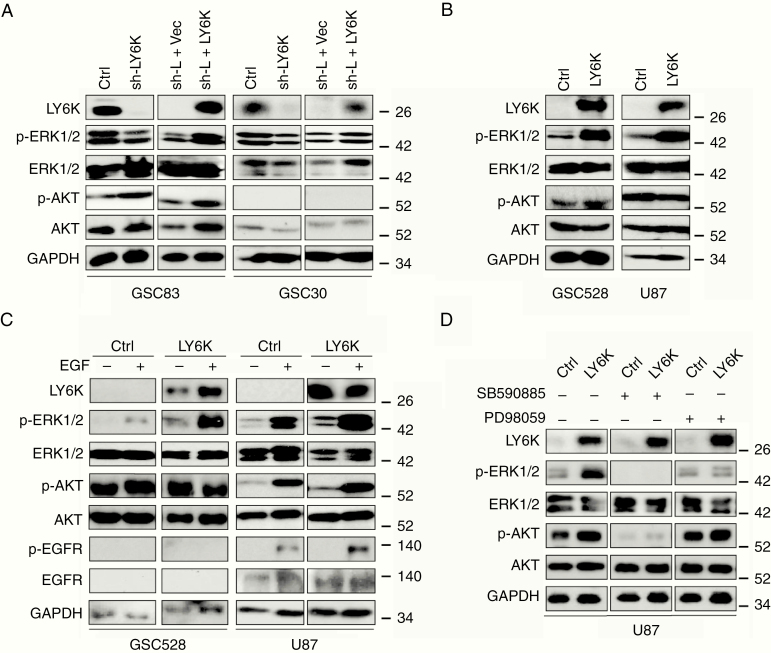
Fig. 3.
LY6K promotes ERK1/2 activation in GBM cells. (A) IB. LY6K knockdown decreased pERK1/2 levels in GSC83 (left) and GSC30 (right) cells, while subsequent expression of exogenous LY6K restored p-ERK1/2 levels. (B) IB. Exogenous expression of LY6K enhanced p-ERK1/2 in GSC528 (left) and U87 cells (right) with otherwise undetectable levels of LY6K. (C) IB. EGF further increased LY6K-enhanced p-ERK1/2 levels in GSC528 and U87 cells with exogenous LY6K expression. No notable changes in p-EGFR/EGFR were observed. (D) IB. RAF inhibition by SB590885 eliminated p-ERK1/2 expression, while MEK inhibition by PD98059 blocked LY6K-enhanced ERK1/2 signaling. For all IB, p-AKT/AKT were used as nonspecific proteins and GAPDH was a loading control. Data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results.