Figure 5.
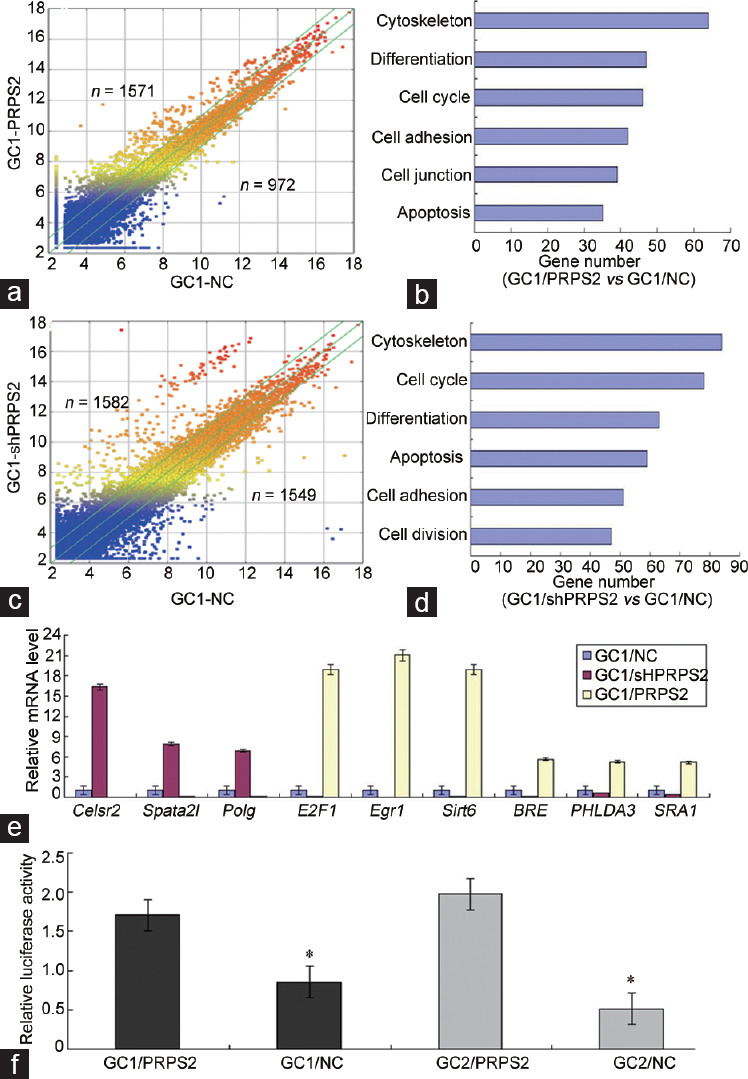
The potential genes and pathways regulated by PRPS2 were identified in GC1 cells. (a) Scatter diagram of the differential genes in GC1/PRPS2 and GC1/NC cells. (b) Potential signaling pathways of the differential genes in GC1/PRPS2 and GC1/NC cells. (c) Scatter diagram of the differential genes in GC1/shPRPS2 and GC1/NC cells. (d) Potential signaling pathways of the differential genes in GC1/shPRPS2 and GC1/NC cells. (e) Nine genes associated with cell apoptosis signal were confirmed in GC1 cells by qRT-PCR. (f) Transcriptional activity of E2F1 was measured by Luciferase Reporter Assay. *GC1/NC versus GC1/PRPS2 and GC2/NC versus GC2/PRPS2, P < 0.05 by independent-samples t-test. PRPS2: phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphate synthetase 2; NC: negative control; qRT-PCR: quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; Polg: polymerase (DNA directed), gamma; E2F1: E2F transcription factor 1; Egr1: early growth response 1; BRE: brain and reproductive organ-expressed; PHLDA3: pleckstrin homology-like domain family A member 3; SRA1: steroid receptor RNA activator 1.
