Figure 2.
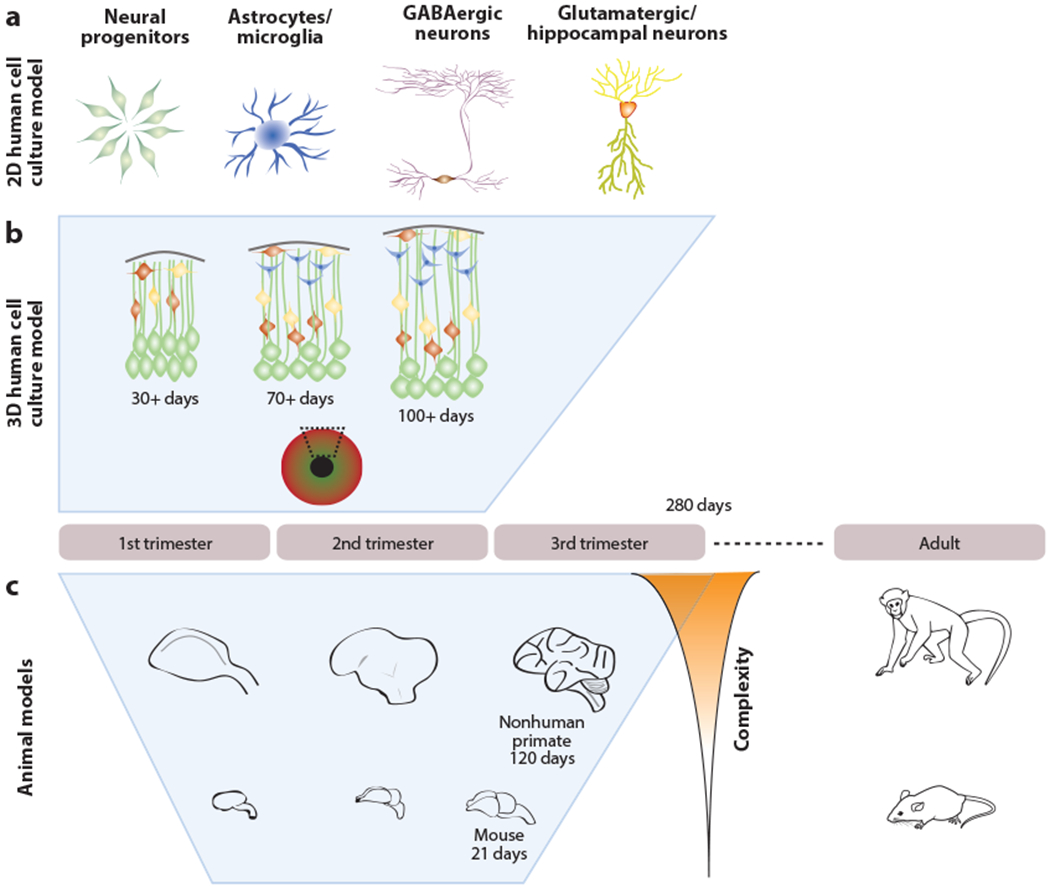
Models of disease using human cell culture and animals. Human induced pluripotent stem cells and animal models capture different properties of brain development and function. (a) 2D cultures of specific cell types can reveal cell type-specific tropism and mechanisms and can also be used to identify quantifiable phenotypes for drug screening and diagnostics. (b) 3D cerebral organoids can mirror morphological and transcriptional dynamics through the first two trimesters of pregnancy. (c) Animal models can be used to investigate the entire gestational period but have species-specific end points of neural complexity and different timescales that may limit the fidelity to human development. Behavioral effects and the impact of viral infections on the adult organism can be modeled using animals.
