Fig. 1.
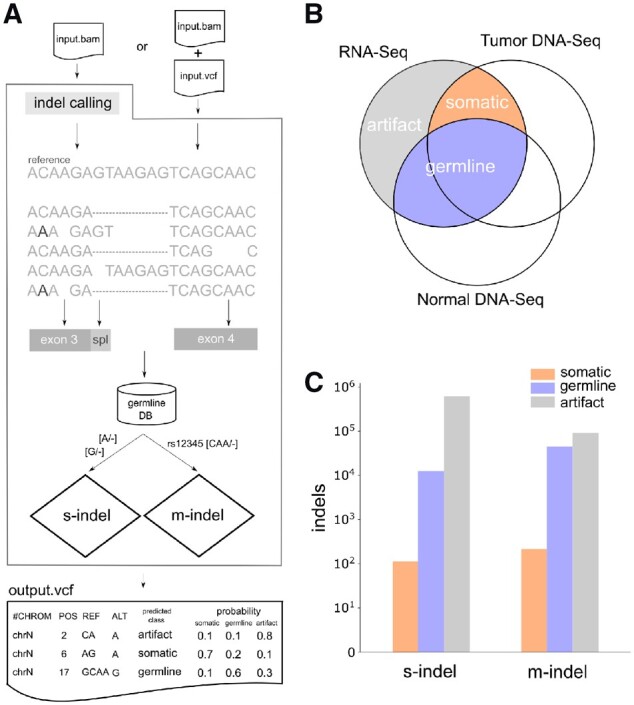
Computational framework and training dataset construction. (A) Workflow of RNAIndel. A tumor RNA-Seq BAM file is a required input. If an optional VCF file from user’s variant caller is supplied, indel calls in the file are used for prediction. Otherwise, indel calling is performed on the input BAM file using the built-in caller. Features are calculated using alignment pileup, transcript structure, and database. Alignments are spliced (dashed) and may contain non-reference variations which alter the indel flanking sequence (C > A at the 2nd base). Indels are annotated for coding exon (grey box) and splice region (light-grey box), defined as an intronic region within 10 bp of the exon boundary. After annotating a germline database membership, single-nucleotide (s-indel) and multi-nucleotide (m-indel) indels are separately predicted using random forest classifiers specifically trained for each type. Predicted class is based on the highest probability of being somatic, germine or artifact. RNAIndel outputs an annotated VCF file. (B) Training set generated from 330 cases. Indel calls in RNA-Seq were classified somatic, germline and artifact by matching with T/N-paired WES and WGS (DNA-Seq) data. (C) The s-indel and m- indel distribution in the categories of somatic, germline and artifacts. The class distribution of each dataset is shown in logarithm scale
