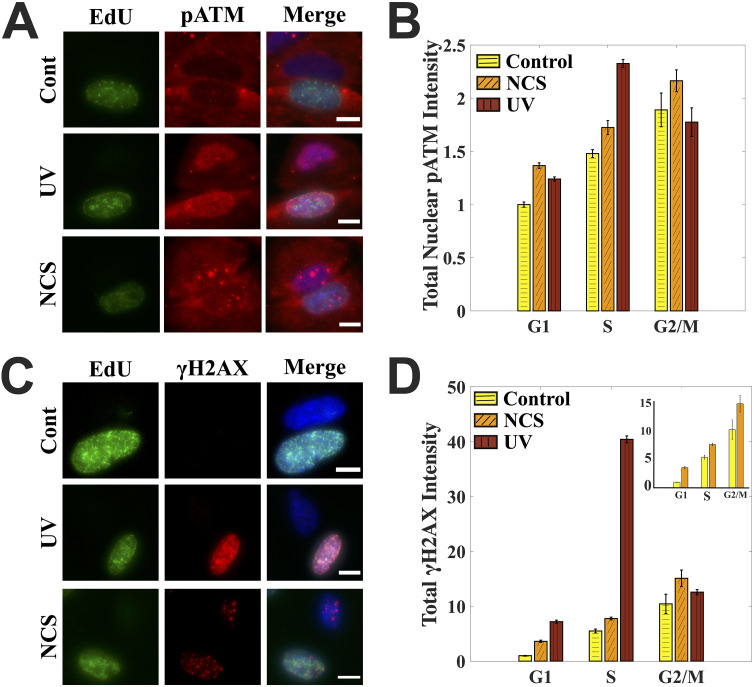
FIG 1.
Cell cycle-dependent DNA damage responses. (A) Cell cycle-dependent induction of pATM after UV and NCS treatment. Each row has two cells: one S phase (EdU positive) and the other non-S phase. Merged images also have a DAPI channel shown here in blue. Images were processed the same to aid the comparison. (B) Quantification for panel A. UV-treated cells have a pATM peak in the S phase, while NCS-treated cells have pATM levels that increase with the increase in DNA content through the cell cycle. (C) Cell cycle-dependent induction of γH2AX after UV and NCS treatment. Each row has two cells: one S phase and the other non-S phase. Merged images also have a DAPI channel shown here in blue. Images were processed with the same contrast adjustments to aid the comparison. (D) Quantification for panel C. UV-treated cells have a sharp γH2AX peak in the S phase, while NCS-treated cells have pATM levels that increase with the increase in DNA content through the cell cycle. The inset compares γH2AX levels just for the control and NCS-treated cells. DNA damage in cells was caused with either 1.6 μg/ml NCS for 2 min or 10 J/m2 UV, after which cells were left to recover for 60 min. Control cells were fixed right after EdU labeling. Bar graphs are normalized with respect to the mean value for G1 phase in control cells across the populations. Error bars are standard errors of the mean. Scale bars: 10 μm. See also Fig. S1 in the supplemental material.