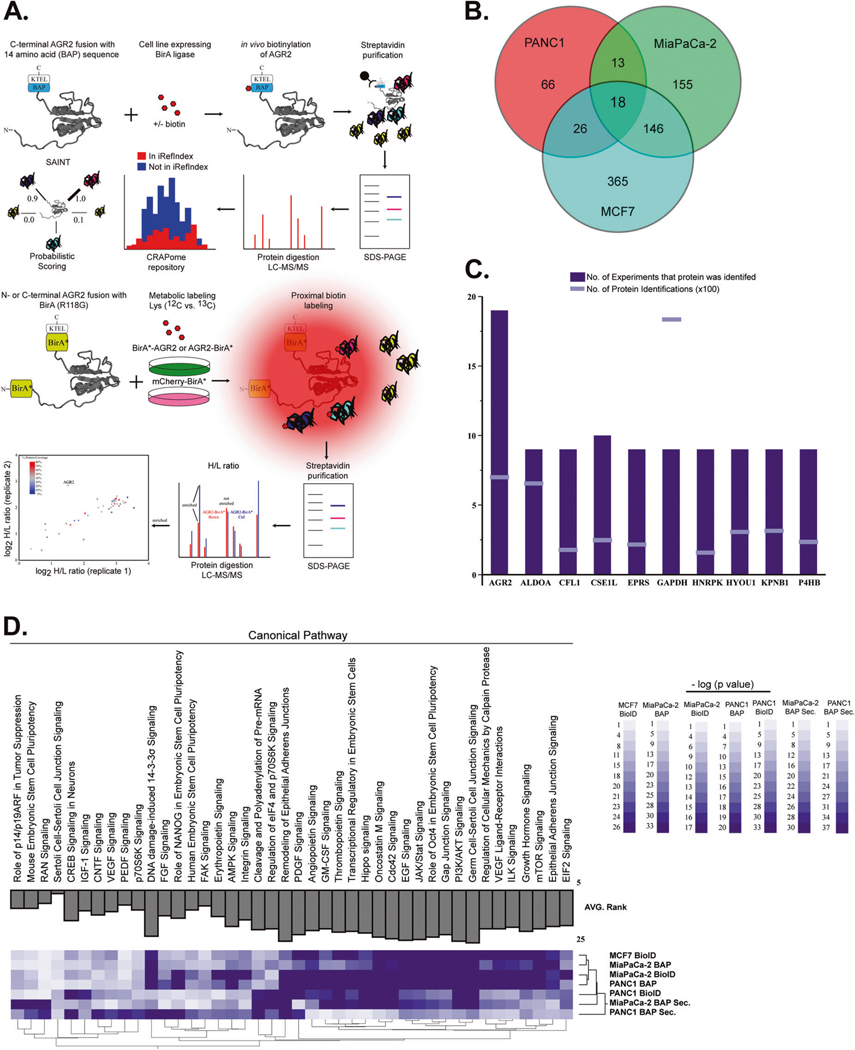
Fig. 2.
Interrogation of AGR2-interacting partners in the ER and extracellular space. A We performed immunoprecipitation assays followed by mass spectrometry (MS) analysis of BAP-AGR2 and AGR2-BAP. Protein lists were submitted to CRAPome (contaminant repository for affinity purification) and SAINT (significance analysis of INTeractome) [54] analysis, which allowed the identification of high-scoring interactions. We also used proximity ligation of biotin to prey proteins by the expression of bait proteins fused to a nonspecific biotin ligase, BirA* (BioID). In vivo biotinylation of proximal proteins was detected by streptavidin-based affinity purification and proteomics identification. Isotopic labeling of cells with control (BirA* mCherry) transfected cells was used to refine proteins in the AGR2 interactome. B Total number of AGR2-interacting proteins after removal of contaminants. C AGR2 was identified in (n = 19/19) experiments derived from whole-cell lysates (although its expression levels were lower than high abundant contaminant proteins) (GAPDH). D New biological pathways ascribed to AGR2 were enriched by ingenuity pathway analysis. The AGR2 interactome was enriched for proteins that have been linked to the mTORC pathway in all three cancer cell lines used in this assay. We also noted that analysis of the AGR2 interactome in the extracellular (Secreted) space clustered differently that the whole-cell lysates (whole-cell lysates)