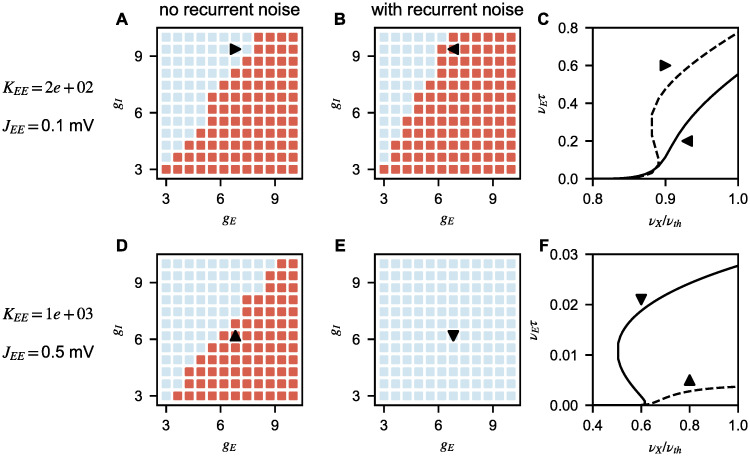
Fig 7. Role of recurrent noise in generating multiple solutions at onset in model B.
Number of solutions for different combinations of gE and gI (red and blue correspond to single solution and multiple solutions, respectively) computed without (first column) and with (second column) recurrent noise; the third column shows transfer functions for specific combinations (indicated by triangles in the first two columns). Both for small (first row) and large (second row) K, noise influences the number of solutions. (A-C) For some parameters, noise reduces the size of the region with multiple solutions. (D-F) For others, noise increases the size of the region with multiple solutions. Parameters: JIE = JEE, gIX = gEX = 1, αI = αE = 1.