Figure 1.
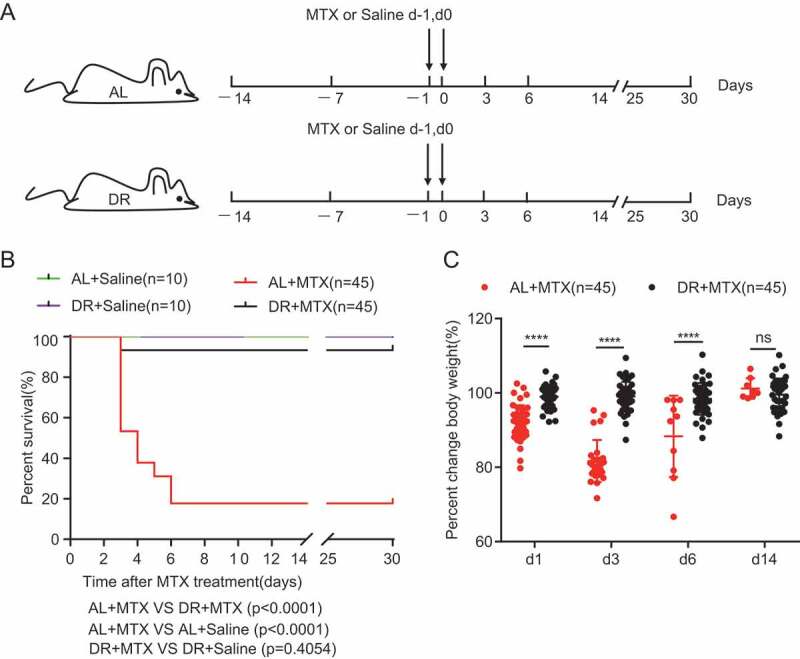
DR significantly improves survival rate and body weight maintenance of mice exposed to lethal doses of MTX treatment. (A) Scheme of experiment. Two-month-old mice were fed with AL diet or 30% DR diet for 14 days before MTX administration and the diet regimen was continued afterward. Then, mice were intraperitoneally injected with saline as control or MTX for 2 days at a dose of 120mg/kg (d-1) and 60mg/kg (d0). (B) Survival was monitored daily after MTX administration. (Data combined from 3 independent experiments. n = 45 mice per group for the AL+MTX mice and DR+MTX mice; n = 10 mice per group for the AL+Saline mice and DR+Saline mice) Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon test. (C) Percent change of body weight at indicated timepoints after MTX treatment compared to before MTX treatment (n = 45 mice per group, combined from 3 independent experiments). Note that the majority of mice were dead within 7 days after MTX administration, therefore, the number of mice measured in the AL group was much reduced at later timepoints after MTX treatment. Unpaired two-tailed, Student’s t test. Results were displayed as mean±SD. n.s: nonsignificant; ****: P < .0001. AL: mice on AL diet; DR: mice on DR diet; AL+Saline: mice on AL diet and received saline injection; DR+Saline: mice on DR diet and received saline injection; AL+MTX: mice on AL diet and received MTX injection; DR+MTX: mice on DR diet and received MTX injection.
