Figure 6: The sorafenib (S) and quinacrine (Q) combination improves the survival of mice subjected to a thyroid orthotopic injection of ATC cells.
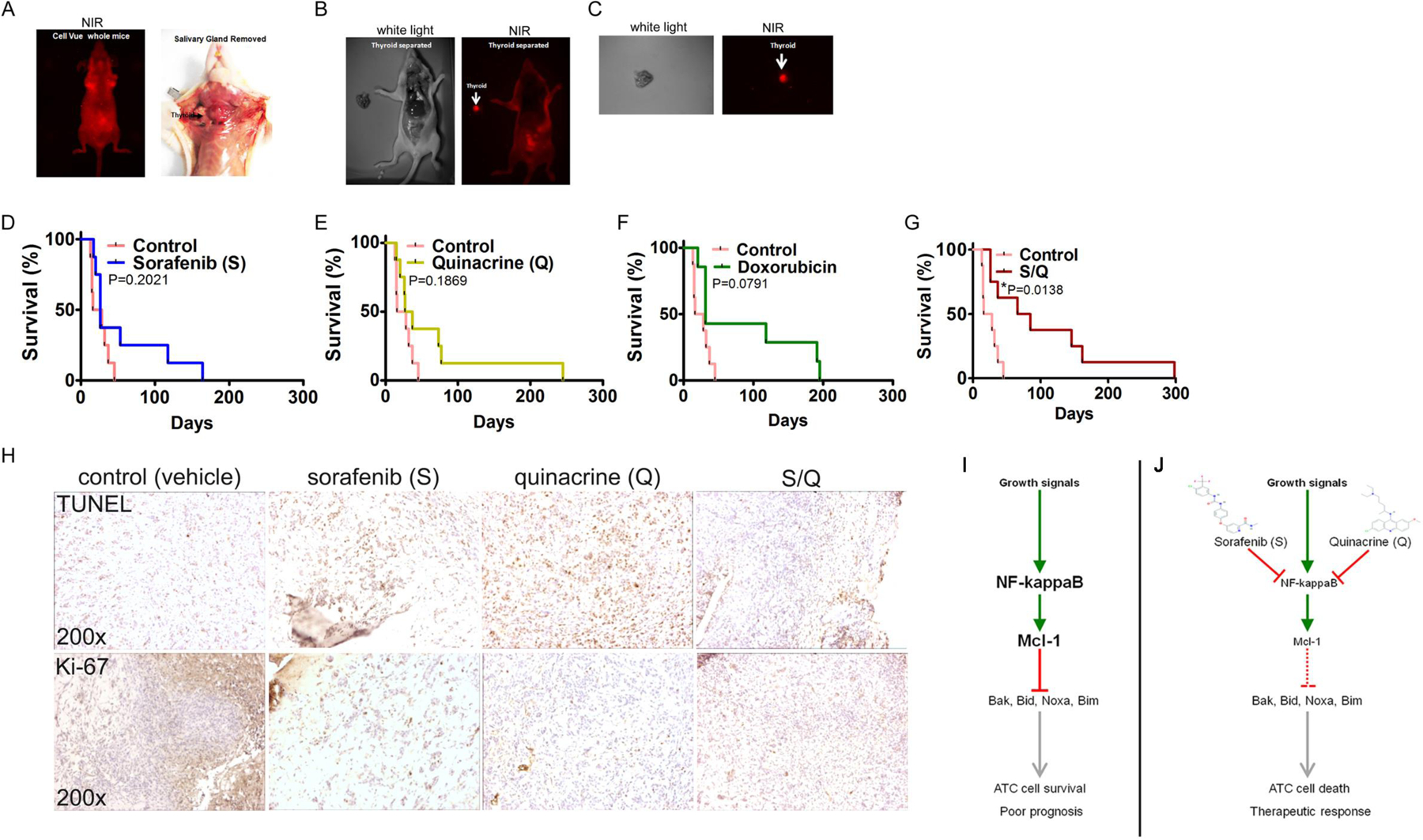
(A) Live whole-body near-infrared imaging (NIR) of whole mice (left panel) and tumor engraftment of 8505C cells in the thyroid of a Nu/Nu mouse (right panel). (B) NIR-imaging of a Nu/Nu mouse subjected to thyroid orthotopic injection of CellVue® NIR815-labeled 8505C cells after the removal of the salivary gland. (C) NIR-imaging of a dissected and isolated tumor ATC-xeno-engrafted mouse (Nu/Nu) thyroid. The injected 8505C cells were labeled with CellVue® NIR815-labeled Survival curves of mice subjected to thyroid orthotopic injection of 8505C cells and subjected to no treatment (Control) and sorafenib (D), quinacrine (E), doxorubicin (F) and the combination of S and Q (G). (H) Immunohistochemistry for TUNEL (apoptosis) and Ki-67 (proliferating cells) on mouse thyroid xenograft tumors of the ATC cell line 8505C. (I) Growth signals trigger constitutively active NFκB signaling and Mcl-1 expression in ATC cells. Mcl-1 inhibits the activity of the pro-apoptotic proteins Bak, Bid, Noxa and Bim. In addition, Mcl-1 may also influence cell cycle progression and proliferation (not depicted). (J) Both S and Q inhibit NFκB activity and ameliorate Mcl-1 expression. Selectivity of the compounds is achieved through increased activity of NFκB in ATC’s. Reduced expression of Mcl-1 allows the pro-apoptotic proteins Bak, Bid, Noxa and Bim to trigger cell death (apoptosis) and a therapeutically relevant anti-tumor response in ATC.
