Figure 2.
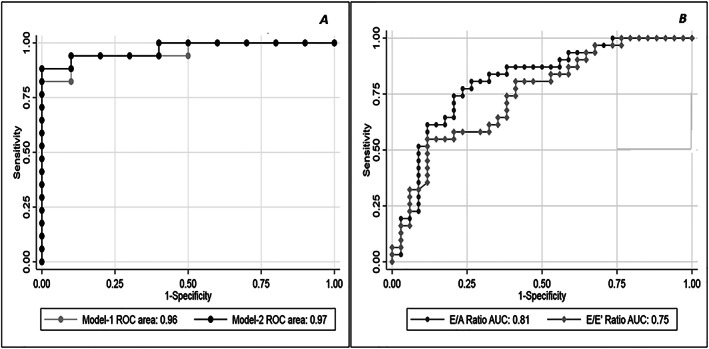
Multivariable logistic regression analysis. (A) Two models with similar accuracy in detecting PCWP >15 mmHg were identified Model 1 included TR velocity, LAVi, and E wave velocity, and had ROC‐AUC = 0.98; 95% CI [0.95, 1.00]. An alternative model excluding TR velocity from the analysis was tested: Model 2 included AT RVOT, LAVi, and GLS 4ch, reaching a ROC‐AUC = 0.96; 95% CI [0.91, 1.00], similar to Model 1 (P value of the ROC comparison = 0.46). (B) Multivariable logistic regression analysis: EA ratio and E/e' accuracy in detecting PCWP >15 mmHg. AT RVOT, acceleration time at right ventricular outflow track; CI, confidence intervals; E/A, peak e‐wave velocity/peak a‐wave velocity ratio; E/e' peak, e‐wave velocity divided by mitral annular e' velocity (average); E wave, peak mitral e‐wave velocity; GLS 4ch, global longitudinal strain in four chamber view; HFrEF, heart failure and reduced ejection fraction; LAVi, left atrial volume indexed; PCWP, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure; ROC‐AUC, receiver operating characteristic‐area under the curve; TR velocity, tricuspid regurgitation peak velocity.
