Figure 1.
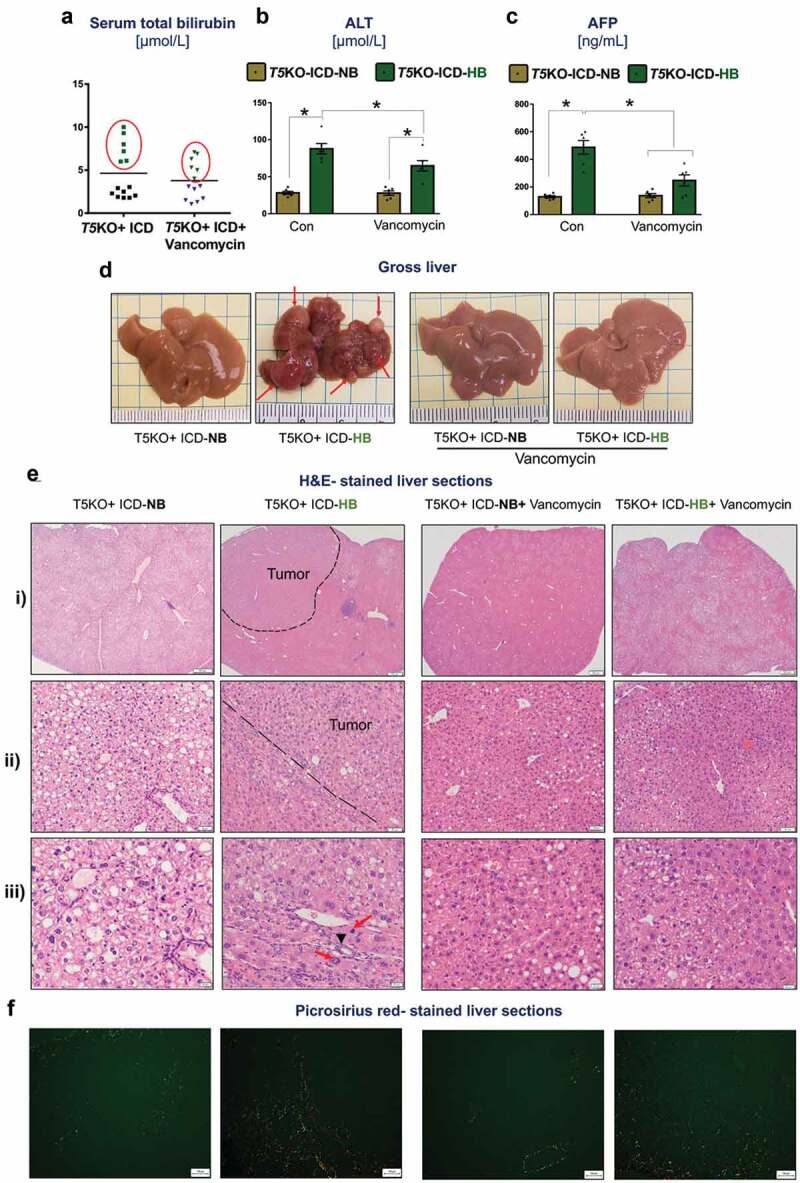
Vancomycin blocks inulin-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Inulin containing diet (ICD)-fed T5KO mice were maintained either on regular drinking water or water containing vancomycin (0.5 g/L). (a) total serum bilirubin. Based on serum bilirubin levels, mice were stratified into normal bilirubin (NB) or high bilirubin (HB, denoted by green dots present in red circle) groups. (b–c) serum levels of B) alanine transaminase (ALT), an enzyme predominantly present in liver and (c) alpha-fetoprotein, a tumor marker. (d) Representative macroscopic photographs of liver. Red arrows point to HCC nodules. Histological analysis (Hematoxylin and Eosin staining) of the liver: E i–ii) Dotted line demarcates the tumor from the non-tumor containing region. (e-iii) black arrow indicates the presence of bile ducts in the tumor region, and red arrows denote mitotic figures. (f) Collagen staining by picrosirius red. Data are representative of six mice per group. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. ANOVA, *p < .05.
