Figure 2.
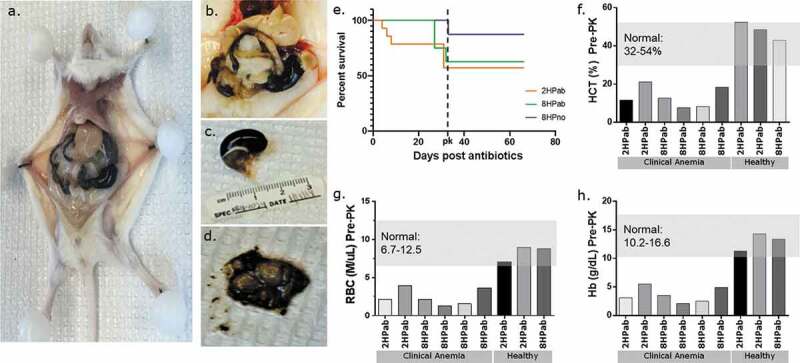
Antibiotic therapy promotes clinical anemia, but phylloquinone supplementation restores normal CBC values. (a–d) Necropsy photos from clinically anemic mice. (a, b) Gross pathology of euthanized, moribund mouse. Livers present acute pallor and gastrointestinal tract is filled with hemorrhagic contents. (c) Significantly distended stomach filled with hemorrhagic contents. d) Incised stomachs exposing unclotted, digested blood content. (e) Kaplan-Meier plot showing mortality following the last antibiotic treatment (day 0). Following PK supplementation (dotted line), no further mortality was observed. (f–h) CBC results of six clinically ill and three healthy mice prior to vitamin K treatment. Each column represents an individual mouse. Mice showing clinical signs of lethargy, pallor, and dullness had hematocrit (HCT), red blood cell (RBC) and hemoglobin (Hb) values consistently lower than established reference ranges in mice. Clinically healthy mice had CBC values within normal reference ranges.
