Figure 6.
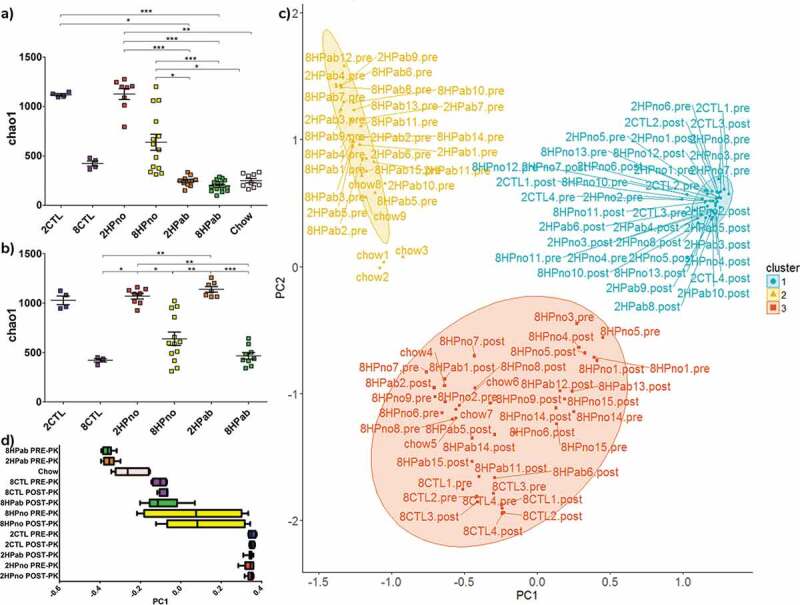
Antibiotics and folate affect alpha and beta diversity in the fecal microbiome. (a–b) Alpha diversity plots. (a) In PRE-PK mice, decreased alpha diversity is associated with both 8 mg folate/kg diets, conventional chow and antibiotic treatment. (b) In POST-PK mice, the effect of antibiotics is lost, but increased dietary folate reduces alpha diversity. P-values computed using a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by a Dunn’s multiple comparison test. *p < .05, **p < .01, and ***p < .001. (c–d) Principal coordinates analysis. (c) Unweighted UniFrac ordination and d) box plot of PC1 by treatment group highlight differences in fecal microbial communities due to antibiotics and dietary folate. Fecal microbiomes clearly clustered by either antibiotic treatment or dietary folate suggesting effects of both treatments on the microbiome.
