Figure 1.
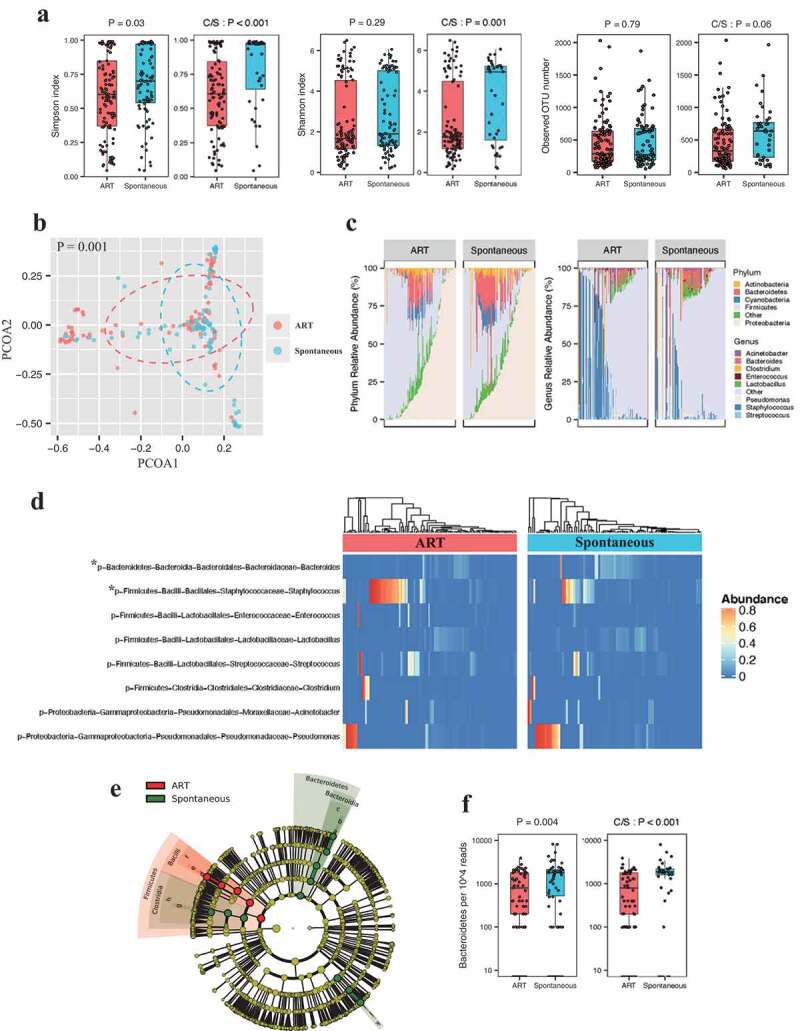
The first meconium microbiome exhibit discrete composition between ART and spontaneous conception groups.
(a) Comparison of α-diversity (Simpson, Shannon index and Observed OTU numbers) between ART versus spontaneous conception groups (and between ART cesarean section and spontaneous cesarean section groups; C/S, cesarean section) using the one-way ANOVA. Boxes indicate interquartile range, lines indicate medians, and whiskers represent range. (b) Comparison of β diversity between ART versus spontaneous conception groups using PERMANOVA based on Bray-Curtis distances. (c) Relative abundance of core bacterial phyla and genera (> 1% mean relative abundance) in the meconium samples from ART and spontaneous conception groups. (d) Heatmap of the core bacterial genera for ART and spontaneous conception groups with corresponding Hierarchical clustering dendrogram. * genera relative abundance is significantly different (P < .05 after Bonferroni Correction) between neonates conceived by ART and following spontaneous conception. (e). Linear discriminant analysis of taxa enrichment between ART versus spontaneous conception groups. Criteria: Alpha value for the factorial Kruskal-Wallis test among classes < 0.05; Alpha value for the pairwise Wilcoxon test between subclasses < 0.05; LDA score for discriminative features > 4. (f). Relative abundance of Bacteroidetes (normalized to 10,000 read counts) between ART versus spontaneous conception groups (and between ART caesarean section and spontaneous caesarean section groups).
