Figure 1.
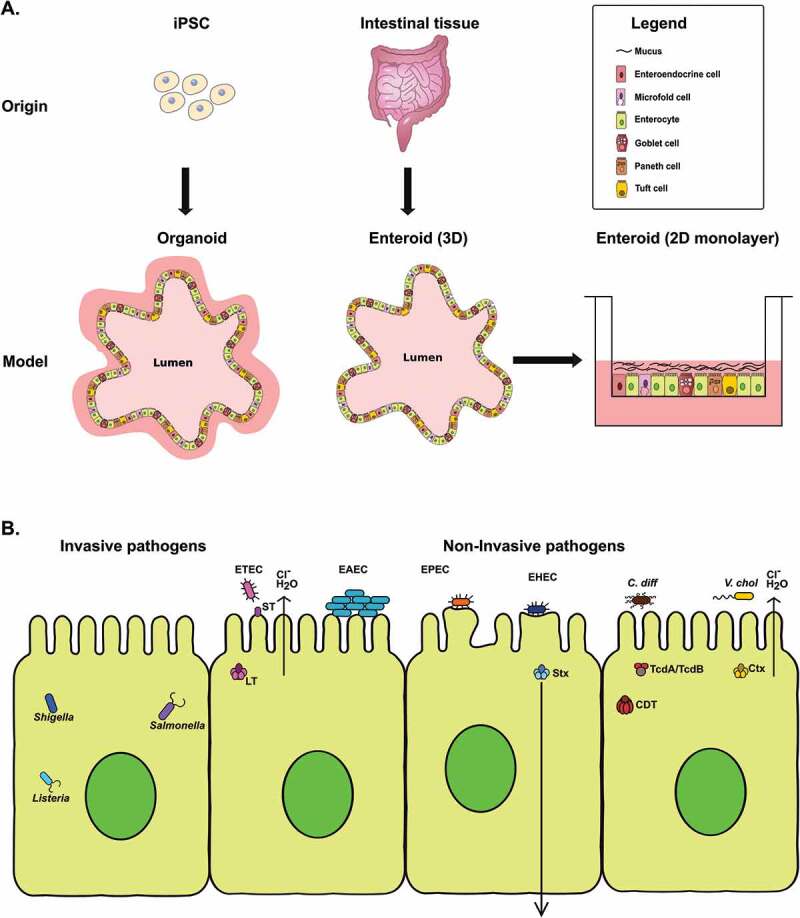
(a) Illustration of the origin and lineage composition of organoids and enteroids. Organoids are derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and contain cells of epithelial and mesenchymal lineages. Enteroids are derived from intestinal tissue and contain cells of epithelial lineage only. Both enteroids and organoids contain multiple epithelial cell types. (b) Schematic diagram showing an outline of the molecular pathogenesis mechanisms of invasive and noninvasive enteric bacteria in organoids and enteroids discussed in this review. Invasive bacteria such as Shigella, Salmonella and Listeria infect and gain entry into the epithelial cells whereas noninvasive bacteria such as pathogenic E. coli, C. difficile and V. cholerae exert their effect on epithelial cells via toxins or effectors.
