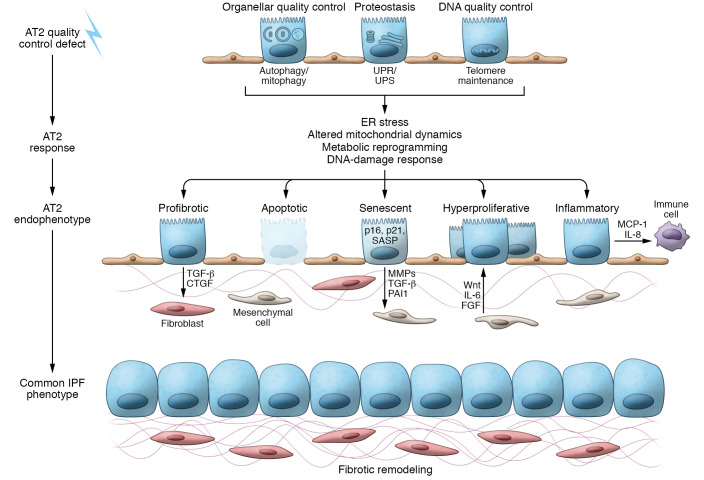
Figure 3. Cell quality control dysfunction and resulting endophenotypes that contribute to fibrotic remodeling.
AT2 cell quality control defects: Effective AT2 cell quality control relies on management of malformed or misfolded proteins (proteostasis), degradation of dysfunctional organelles, and maintenance of telomere length. AT2 response: The loss of quality control involves AT2 cell adaptive compensations, such as activation of the UPR/UPS to regain proteostasis. However, sustained quality control defects lead to cellular disruption and injury from ER stress, persistent mitochondrial dysfunction, metabolic reprograming, and DNA damage responses. AT2 endophenotypes: Modeling AT2 cell quality control defects and interrogation of the IPF epithelia have identified a number of AT2 cell endophenotypes in the fibrotic lung. These include the production of profibrotic mediators including TGF-β, loss of AT2 cells through apoptosis, challenges to progenitor cell function resulting in the loss of progenitor capacity from senescence or emergence of hyperproliferative AT2 cells, and recruitment of immune cell populations. Common IPF phenotype: The resultant loss of alveolar architecture in IPF is defined by fibrotic remodeling and myofibroblast expansion into fibroblastic foci and hyperplasia of lung epithelial cells.