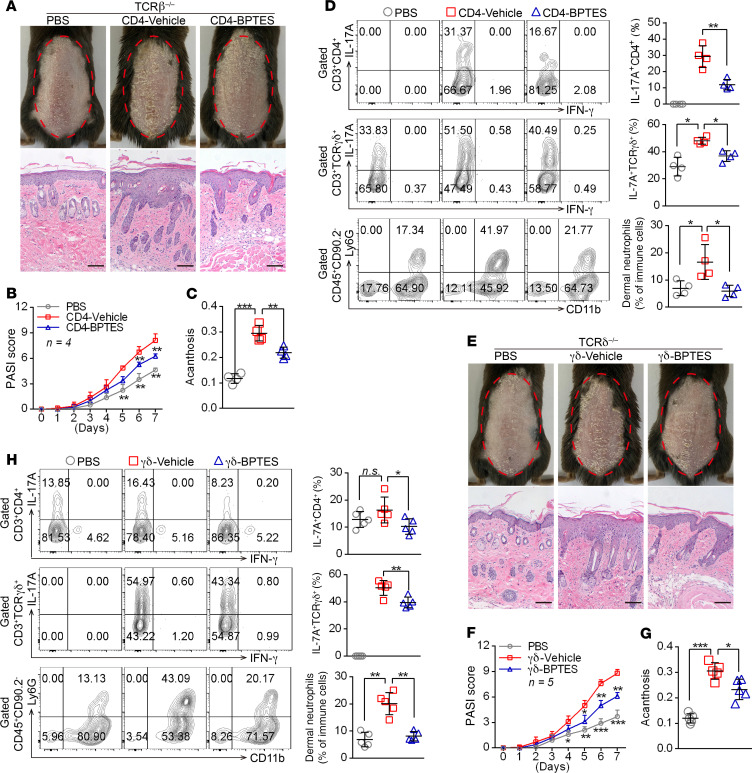
Figure 4. GLS1-mediated glutaminolysis in T cells is pivotal for IMQ-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation.
(A–D) Tcrb–/– mice were transferred with PBS or naive CD4+ T cells pretreated with BPTES (CD4-BPTES) or not (CD4-Vehicle). (E–H) Tcrd–/– mice were transferred with PBS or naive γδ T cells pretreated with BPTES (γδ-BPTES) or not (γδ-Vehicle). The mice were then subjected to IMQ-induced psoriasis as part of the psoriasis-like mouse model. Representative phenotypic presentation and H&E staining of skin lesions (A and E) (scale bars: 100 μm), PASI scores (B and F), and acanthosis (C and G). n = 4 (B) and n = 5 (F). (D and H) Percentage of IL-17A+ cells in dermal CD4+ T cells (gated on CD3+CD4+ T cells) and γδ T cells (gated on CD3+ γδTCR+ T cells) and of neutrophils in dermal CD45+ lymphocytes. n = 4 (D) and n = 5 (H). Data are presented as the mean ± SD and represent 1 of at least 2 independent experiments with consistent results. A 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparisons test (B–D and F–H) was used to determine statistical significance (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).