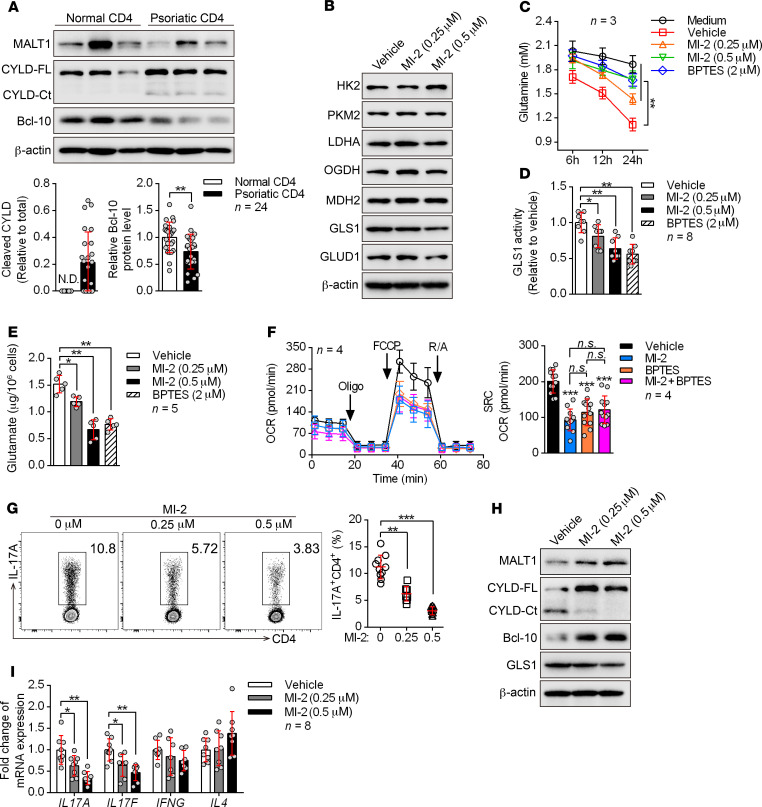
Figure 6. MALT1 protease is consecutively activated and initiates aberrant GLS1-mediated glutaminolysis in psoriasis.
(A) Peripheral CD4+ T cells were collected from healthy donors and patients with psoriasis. Representative blots for the expression level and protease activity of MALT1 (cleavage of CYLD to CYLD-Ct, BCL-10) in CD4+ T cells are shown (n = 3 of a total of 24 samples). CYLD-FL, full-length CYLD; CYLD-Ct, cleaved CYLD. (B–G) Human naive CD4+ T cells subjected to the indicated treatments were polarized into Th17 cells for 5 days. (B) Representative blots show the protein levels of key metabolic enzymes. (C) Consumption of glutamine at the indicated time points. “Medium” refers to glutamine natural degradation (n = 3). (D and E) GLS1 activity (D) (n = 8) and glutamate concentration (E) (n = 5) were measured. (F) Cells were collected to detect the OCR using an extracellular flux analyzer. Cumulative data for the calculated spare respiratory capacity (SRC) are shown (n = 4). Oligo, oligomycin; FCCP, carbonyl cyanide-4 (trifluoromethoxy) phenylhydrazone; R/A, rotenone and antimycin. (G) Percentage of Th17 cells detected by flow cytometry and statistical analysis (n = 10). (H and I) Protein expression of GLS1 (H) and relative mRNA expression of IL17A, IL17F, IFNG, and IL4 (I) (n = 8) in human psoriatic CD4+ T cells treated with MI-2 for 48 hours. Data are presented as the mean ± SD and represent 1 of at least 2 independent experiments with consistent results. A 2-tailed, unpaired Student’s t test (A) or 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (C–G and I) was used to determine statistical significance. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).