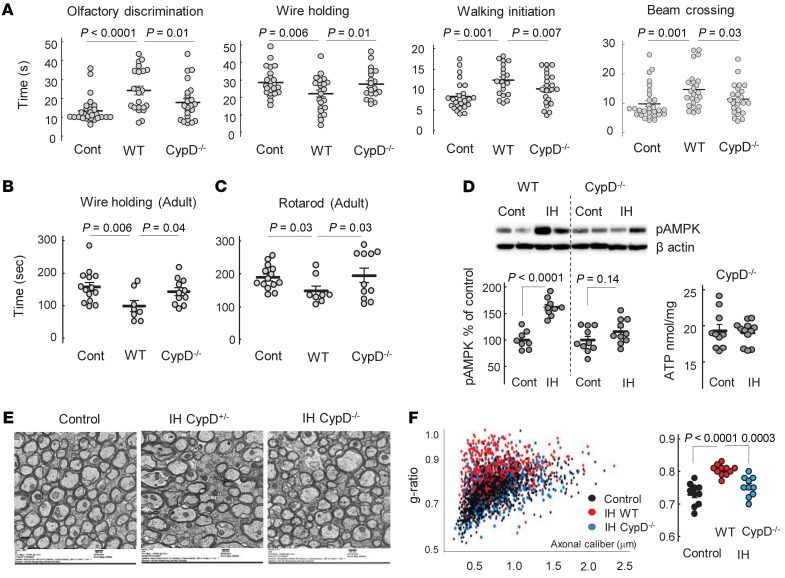
Figure 8. CypD-KO mice are protected against WMI.
(A) Sensorimotor performance of WT and CypD–/– mice after IH exposure in comparison with normoxic controls (combined genotypes). Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s post hoc tests. (B and C) Sensorimotor performance of adult control, WT, and CypD–/– mice exposed to IH stress in their neonatal age. One-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s post hoc test (B) and Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s post hoc tests (C). (D) Western blot analysis of phosphorylated (activated) AMPK in WT and CypD–/– mice and cerebral ATP content in CypD–/– control and IH mice. Unpaired t test. (E) Representative images of electron microscopy of corpus callosum in adult mice of different genotype exposed to neonatal IH stress compared with control (WT). Scale bar: 500 nm. (F) Analysis of axonal g-ratio estimated using electron microscopy images of corpus callosum in adult mice. One-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s post hoc test.