Fig. 1. HA peptide landscape for antibody binding and ADCC function.
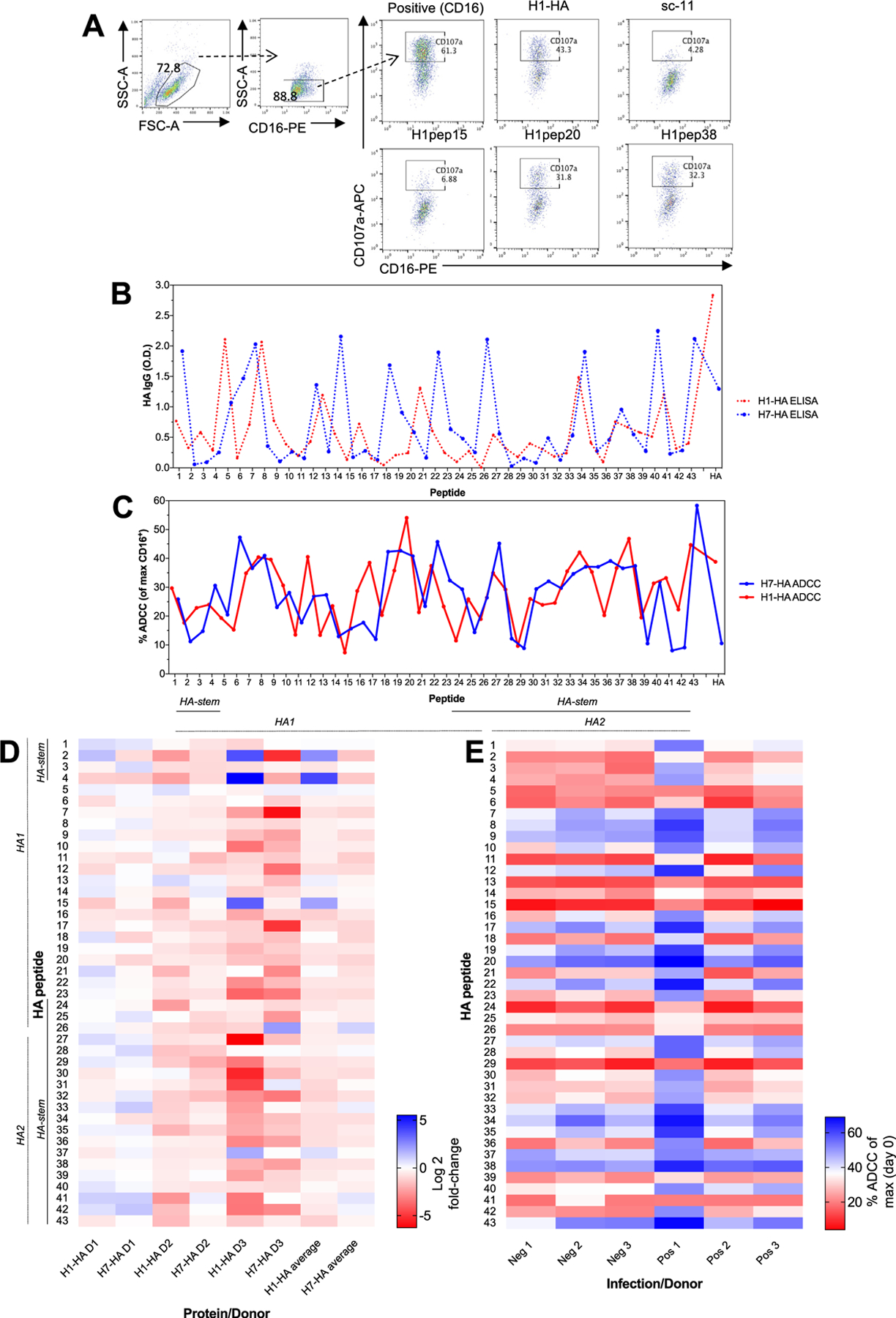
(A) A FACS based NK activation assay was used to assess ADCC antibody responses (representative FACS plots from Positive 1 donor). H1- and H7-HA peptides and full-proteins IgG levels (by ELISA, dotted lines (B)) and ADCC responses (plain lines (C)) (n = 15 human serums). Data represents the mean average. (D) Heat map of fold-change of post- versus pre-H1N1 infection ADCC responses for H1-HA and H7-HA peptides (values are represented as Log2). (E) Heat map of H1-HA peptide ADCC responses (% ADCC (of max CD16+) from (A) for uninfected negative donors (Neg 1–3) and infected positive donors (Pos 1–3). Experiment was repeated twice.
