Fig. 2. Mouse vaccination with high ADCC activating peptides results in partial protection from influenza infection.
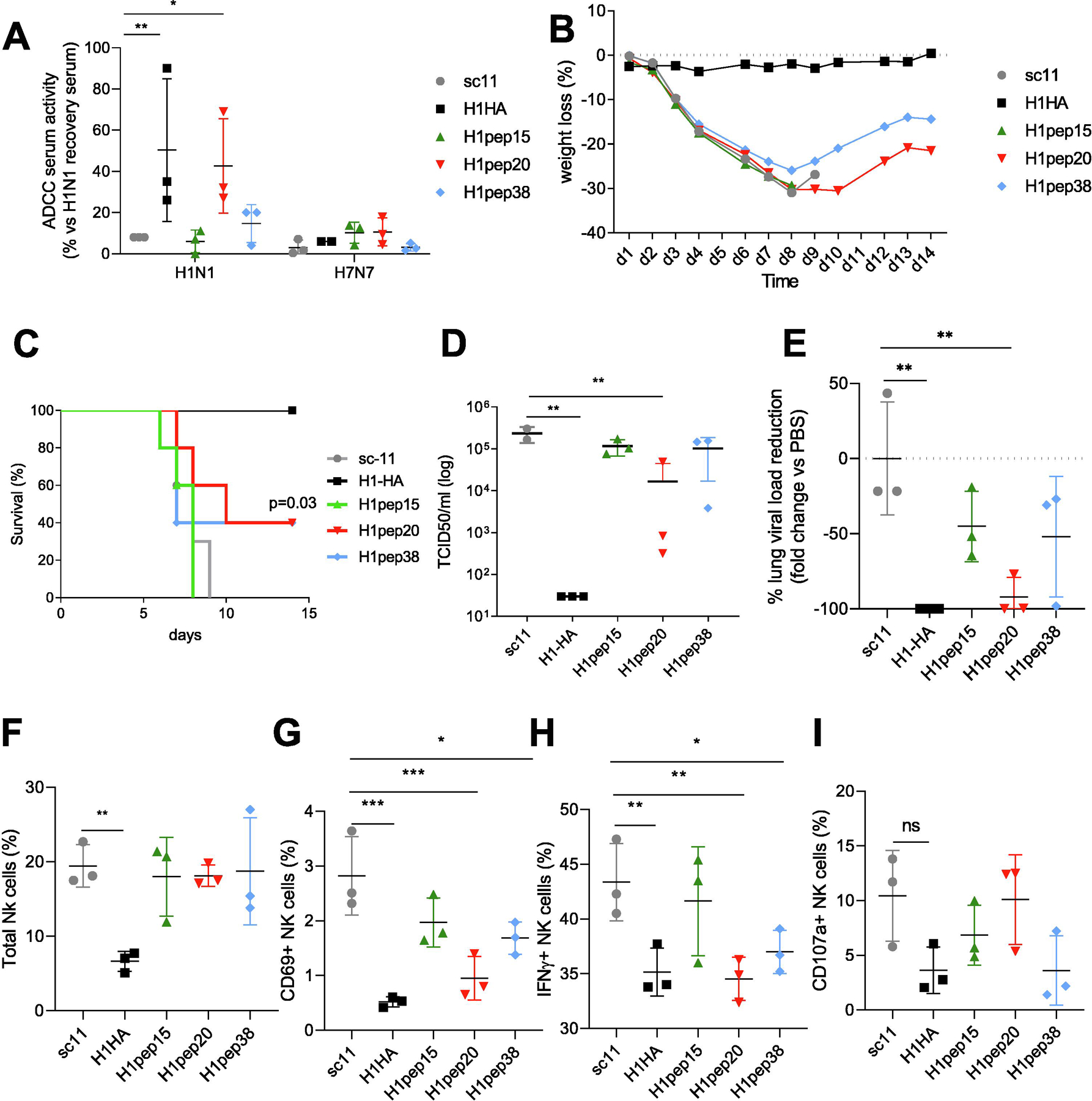
(A) Serum ADCC activity (by NFAT signaling of luciferase reporter NK cells) to H1N1-infected target cells 21 days post-vaccine. Day 14 wt loss (B) and survival (C) of vaccinated mice after lethal H1N1 challenge. TCID50 lung viral titers (D) and fold reduction of lung viral loads (E) at day 7 versus scrambled vaccinated mice. NK cell response in lungs at day 7 post infection for total NK cells (F), CD69+ NK cells (G), IFN-γ+ NK cells (H) and CD107a+ NK cells (I) (see gating FACS plots in Supplementary Fig. 2C). Data represents the mean average and SD. For (A) survival curves were compared for statistical significance with Log-rank Mantel-Cox test (n = 5 per group). For (B–I) data were compared for statistical significance by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test versus scrambled or PBS group, (n = 3 per group) *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005, experiments were repeated twice
