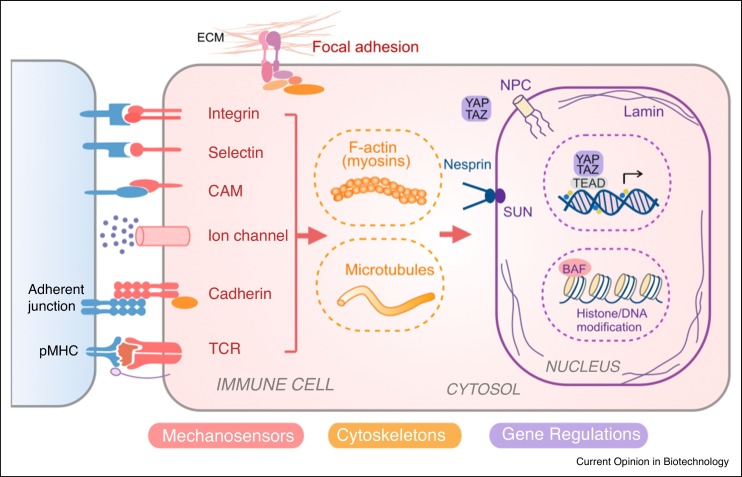
Figure 1.
Mechanotransduction network in immune cells. Immune cells can sense the biophysical cues by receptors including integrins (i.e. LFA-1, Mac-1, VLA-4), selectins (i.e. P-selectin, L-selectin), cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) (i.e. ICAM-1, VCAM), ion channels (i.e. Piezo1), cadherins and T cell receptor (TCR). These signals can be transduced through cytoskeleton (actin, microtubule) and nucleoskeleton (e.g. lamin), and/or converted into biochemical signaling events. The mechanotransduction process not only affects the mechanical structure and property of cell and nucleus, but also regulates immune cell phenotypes and functions via transcriptional factors (e.g. YAP/TAZ) and epigenetic modifications.
*Abbreviation: LFA: Lymphocyte Function-associated Antigen; Mac1: Macrophage-1 Antigen; VLA-4: Integrin α4β1 (very late antigen-4); ICAM: Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1; VCAM: Vascular Cell Adhesion Protein 1.