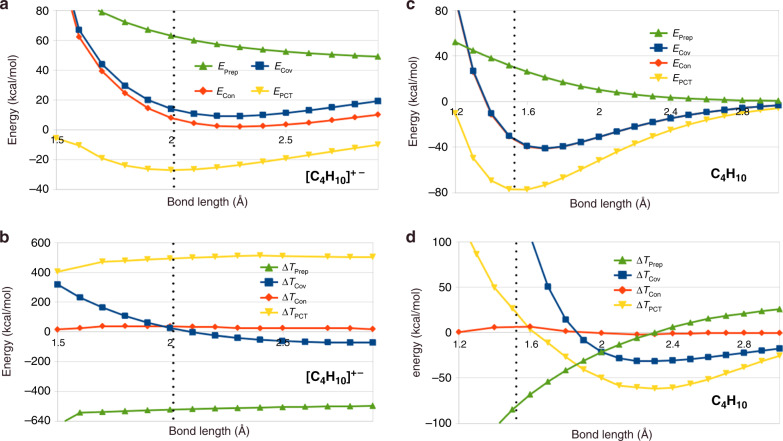
Fig. 2. Energy and kinetic energy changes for 1 and 2 e− C–C bonds.
a Energy decomposition for relaxed dissociation of the central C–C bond in n-butane cation; energy terms are cumulative. b Kinetic energy decomposition for relaxed dissociation of the central C–C bond in n-butane cation; kinetic energy changes, ΔT, are increments. c Energy decomposition for relaxed dissociation of the central C–C bond in n-butane. d Kinetic energy decomposition for relaxed dissociation of the central C–C bond in n-butane. In n-butane, almost half the binding energy occurs due to covalent interaction, but is accompanied by a significant KE increase at the equilibrium geometry (vertical dots). In the weakly bound cation, the KE also increases slightly upon covalent coupling of the fragments at equilibrium. These results are in striking contrast to H and H2 (see Fig. 1).