Figure 3.
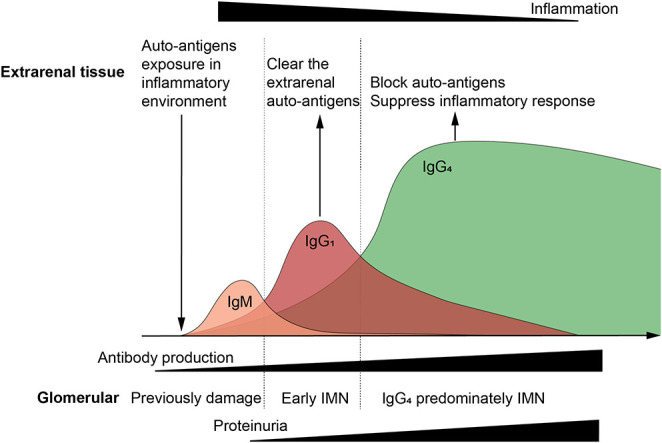
Relationship between extrarenal tissue, immune response, and glomerular damage. Auto-antigens exposure in inflammatory environment induce the auto-immune response, and subsequently immunoglobulins (Ig) undergo class switching. IgG1 mediates the most auto-antigen clearance as the primary effector antibody, and IgG4 blocks auto-antigens as the high affinity anti-inflammatory antibody. When pathogens and auto-antigens are effectively eliminated, the extrarenal inflammatory, and immune responses tend to be alleviated. However, large amounts of antibodies are deposited in the glomeruli, especially IgG4, leading to filtration barrier damage and proteinuria. Extrarenal remission and glomerular damage aggravation were observed, which can be the reason that why idiopathic membranous nephropathy is having trouble finding the primary foci.
