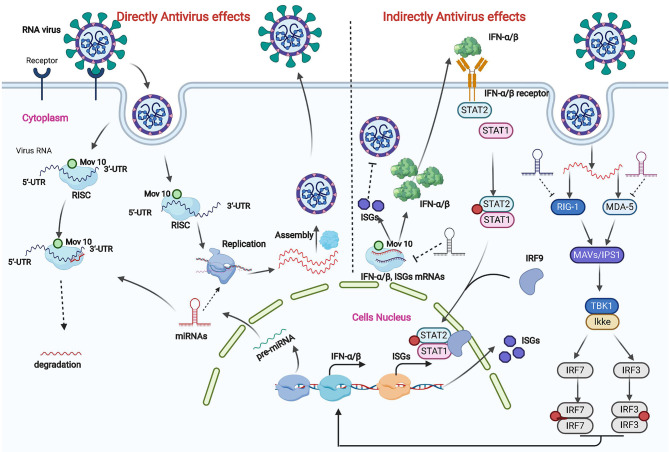
Figure 1.
Direct and indirect antivirus effects of miRNAs in target cells. Antivirus effects of miRNAs are divided into direct and indirect regulation in target cells. In direct regulation, host miRNAs participate in viral RNA degradation in a RISC within a P body in target cells and are also involved in viral RNA replication processes by targeting RNA replication components. Indirect antiviral effects are complex. First, host miRNAs participate in the RIG-1 and MDA-5 pathway-mediated IFN-α/β production. The production of IFN-α/β not only inhibits viral replication in cells but also activates the IFN signal pathway and ultimately causes the expression of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) to decrease virus replication. miRNAs also participate in this regulation process.