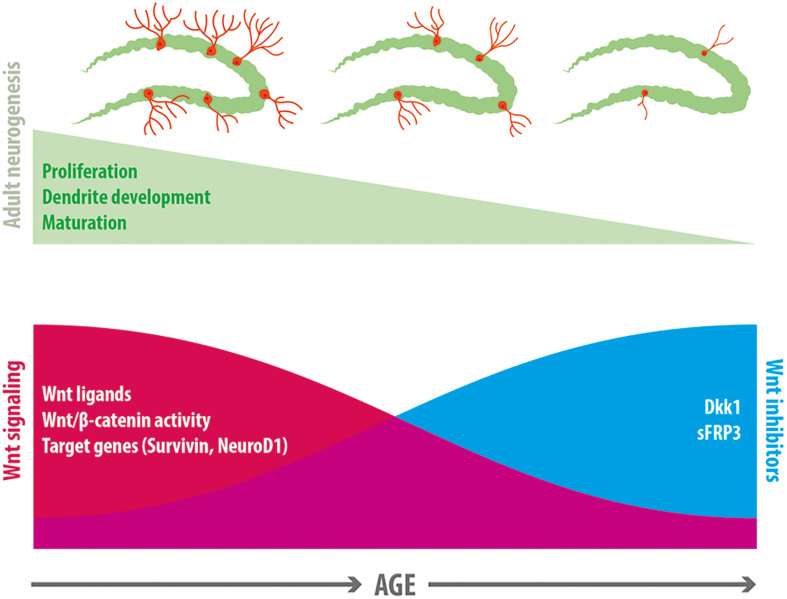
FIGURE 2.
Wnt signaling in the age-related decline in neurogenesis. A reduction in neurogenesis is observed in the dentate gyrus with age, which is accompanied by a decline in proliferation of neural precursor cells, a decreased dendritic development and delayed maturation of adult-born neurons. Evidence exists indicating that a decline in Wnt signaling is associated with this reduction of neurogenesis. In normal aging there is a decrease in the expression of most Wnt ligands in hippocampal astrocytes, a decrease in canonical Wnt signaling activity in the dentate gyrus, and a reduction in the expression of Wnt target genes that control neurogenesis (including Survivin and NeuroD1). Concomitantly, there is an increase in the expression of the Wnt inhibitors sFRP3 and Dkk1 in the hippocampus with age.