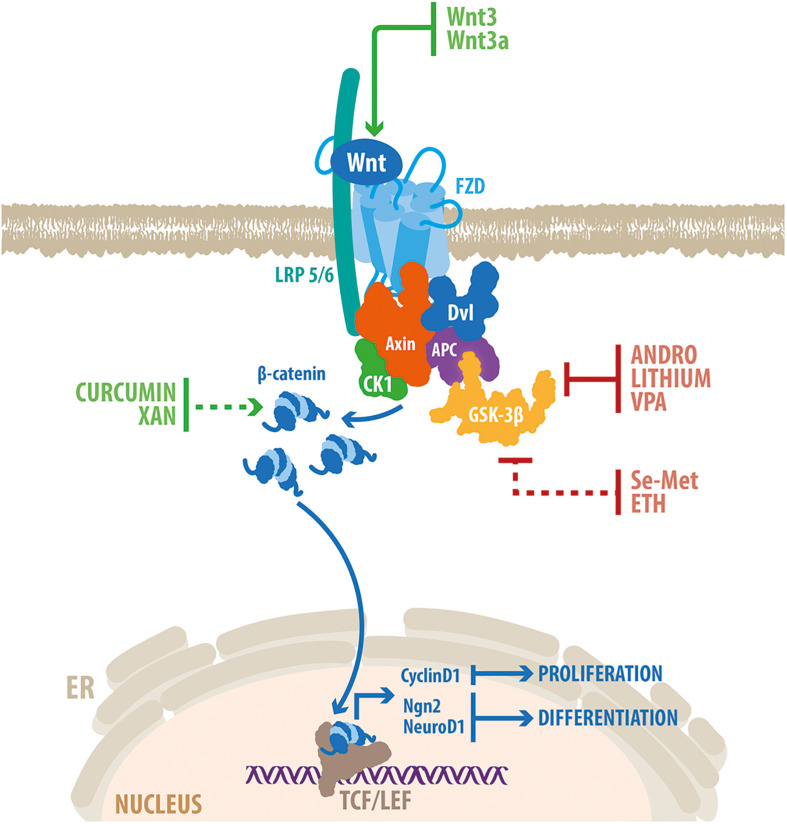
FIGURE 3.
Genetic and pharmacological activation of Wnt/β-catenin promotes neurogenesis in the hippocampus of AD models. Schematic representation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Wnt ligand binds to FZD and LRP5/6, which trigger the recruitment of a multiprotein complex composed also of Axin, APC, CK1 and GSK-3β. This prevents the phosphorylation and degradation of β-catenin that translocates into the nucleus where it binds to members of the TCF/LEF families of transcription factors, to modulate the transcription of target genes. The Wnt/β-catenin signaling components that are target of genetic activation (Wnt3 and Wnt3a) and drugs able to stimulate neurogenesis in the hippocampus of animal models of AD are indicated. Red lines indicate inhibition; green lines indicate activation. Dotted red line indicates GSK-3β inactivation through the PI3K/Akt pathway; dotted green line indicates that the precise mechanism of activation of the Wnt/ β-catenin signaling remains elusive. Some of the drugs (see text for details) have shown to induce the expression of target genes involved in Wnt-mediated induction of proliferation (Cyclin D1) and differentiation (Ngn2 and NeuroD1) in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. VPA, valproic acid; Se-Met, Selenomethionine; ETH, Ethosuximide; XAN, Xanthoceraside.