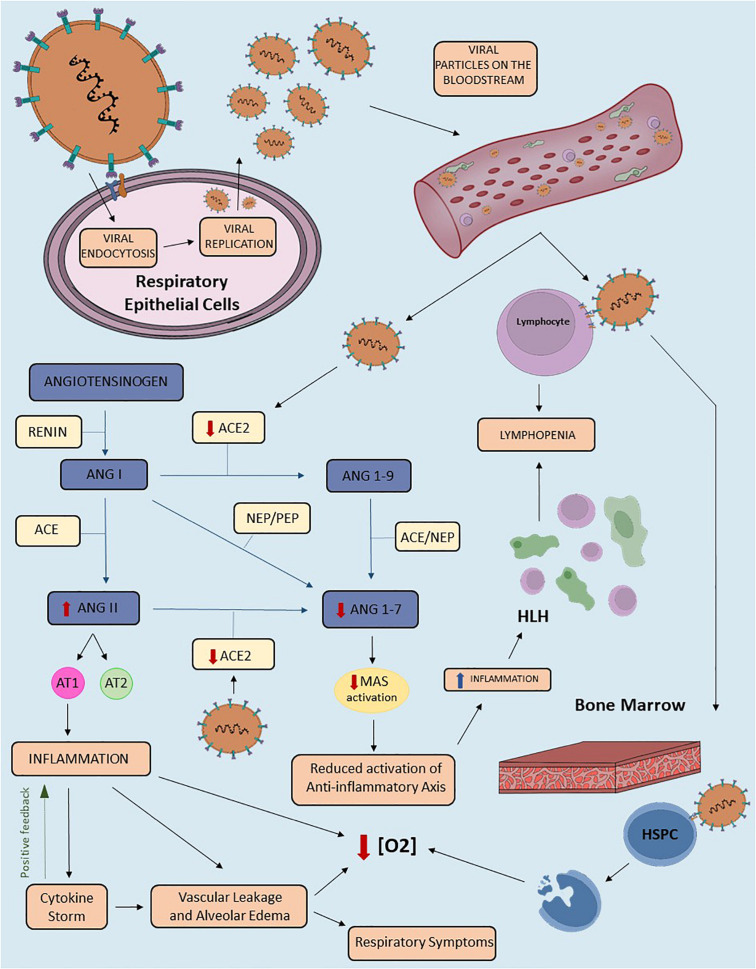
FIGURE 2.
The proposed role of the Renin-Angiotensin System in the pathophysiology of COVID-19. Schematic representation of COVID-19 pathophysiology related to the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) imbalance. This figure highlights the downregulation of transmembrane Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS-CoV-2 infection. The virus enters the host cell after binding to TMPRSS2 and transmembrane ACE2. Viral replication and release from lung cells to the bloodstream enhance viremia, besides diminishing circulating and transmembrane ACE2 levels. The reduction of ACE2 availability results in RAS imbalance due to downregulation of the alternative axis. Consequently, we have an increase in Angiotensin II (Ang II) and decrease in Angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)] levels. The binding of Ang II to the Angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor triggers inflammatory response, including vascular leakage and alveolar edema, both of which can be amplified by Cytokine Storm Syndrome (CSS). This mechanism may contribute to several clinical presentations of COVID-19, including respiratory signs and symptoms. In addition, the downregulation of the ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas receptor axis reduces the anti-inflammatory effects of the alternative RAS axis. Due to ACE2 expression in mature lymphocytes, SARS-CoV-2 may result in lymphopenia. This finding can also be triggered by hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) due to intense tissue inflammation. In addition, the invasion of the bone marrow by the virus, specifically of the hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPC), leads to apoptosis and consequent reduction of oxygen saturation levels. Other mechanisms that may contribute to lower saturation include vascular leakage, alveolar edema and inflammation. ACE2, Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2; TMPRSS2, Transmembrane protease serine 2; RAS, Renin-Angiotensin-System; ANGII, Angiotensin II; ANG(1-7), Angiotensin (1-7); HLH, Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis; HSPC, Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell; [O2], Oxygen concentration; ACE, Angiotensin Converting Enzyme; ANG(1-9), Angiotensin (1-9); ANGI, Angiotensin I; PEP, prolyl-endopeptidase; NEP, neutral-endopeptidase.