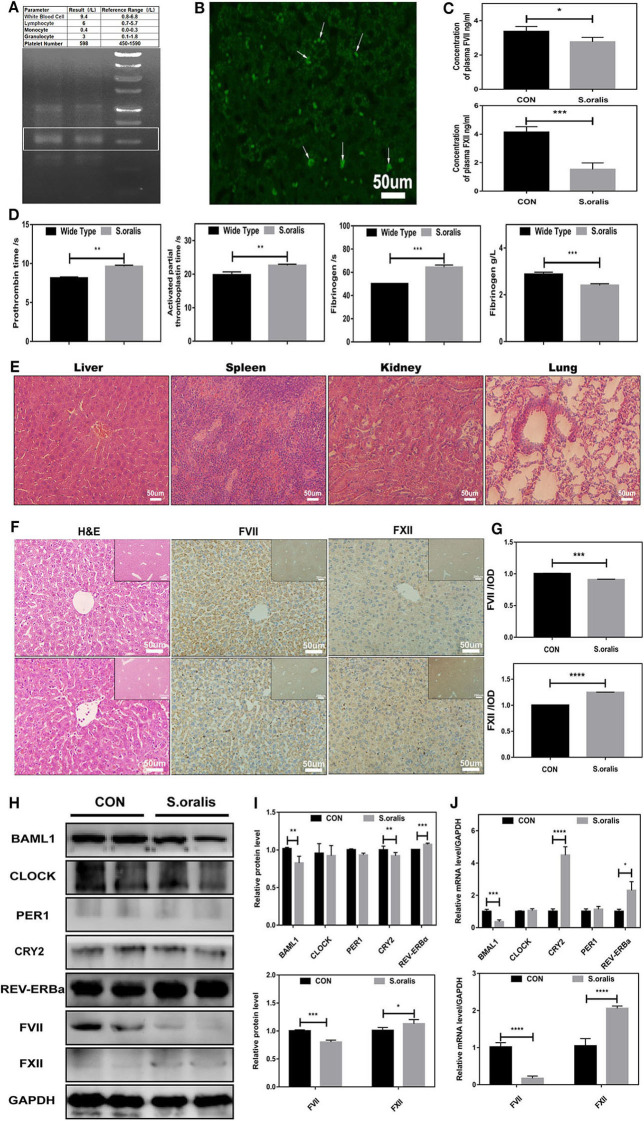
Figure 2.
S. oralis reduced BMAL1 expression and disrupted the biosynthesis of coagulation factors in vivo. Every mouse was infected by S. oralis in about 1 × 108 CFU (colony-forming units) for 24 h. (A) The upper part for the blood routine test of the infected mouse, the lower part for DNA extraction of infected mouse livers. Special primers were designed for S. oralis. (B) FISH for the detection of S. oralis in infected mouse livers. Special primers were designed for S. oralis. Scale bars, 50 mm. (C) Plasma concentration of coagulation factors VII and XII in the infected group as compared to the control group. (D) Routine coagulation array for mice in infected and uninfected groups. (E) H&E staining for liver, spleen, kidney, and lung of infected mice. (F,G) IHC staining for coagulation factors VII and XII of the liver and the relative values of IHC optical density. (H,I) Western blot analysis of circadian clock genes and coagulation factors, and the relative values of densitometry analysis of hepatocytes. (J) qRT-PCR analysis of circadian clock genes and coagulation factors. The experiments were performed three times independently. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 ***P < 0.005; ****P < 0.001.