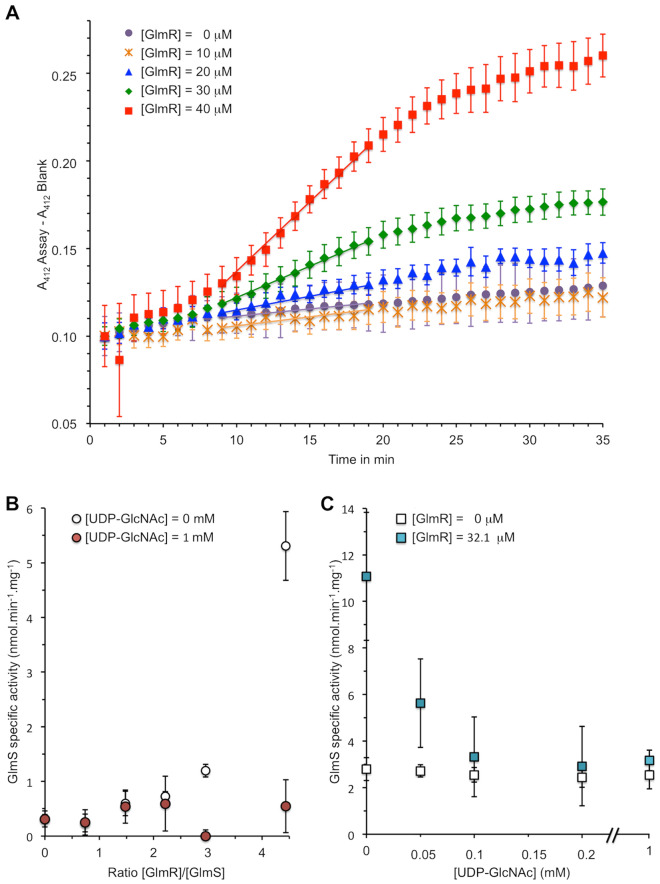
Figure 1.
Measurement of GlmS activity in the presence or in the absence of GlmR and UDP-GlcNAc. Activity of GlmS from B. subtilis was measured by enzyme coupled assay. For each experiment, a reaction without GlmS was performed as negative control and used for background correction. Each experiment was reproduced at least in triplicate and error bars represent standard deviations. (A) Kinetic of GlmS activity in the presence of increasing concentration of GlmR. 7.3 µM of GlmS (48 µg in 100 µl) were incubated in the presence 0, 10, 20, 30 and 40 µM of GlmR in a final volume of 100 µl as indicated in the experimental procedures section. The amount of CoASH produced was monitored at 412 nm during 30 min by microplate reader at 37 °C as described previously20. We observed that the effect of GlmR on GlmS activity is optimal after 8 min of incubation; consequently, to calculate the amount of GlcN6P produced per min by GlmS, we measured the slope between 18 and 8 min. (B) GlmS activity in the presence of increasing amount of GlmR in the absence or in the presence of 1 mM UDP-GlcNAc. 7.3 µM of GlmS (48 µg in 100 µl) were incubated in the presence 0, 5.4, 10.7, 16.1, 21.4 and 32.1 µM of GlmR as indicated in the material and methods section. The amount of CoASH produced was monitored at 412 nm by microplate reader at 37 °C and the specific activity of GlmS was calculated as indicated in Figs. S1 and S2. (C) GlmS activity in the presence of increasing amount of UDP-GlcNAc and in the absence or in the presence of GlmR. 5.3 µM of GlmS (35 µg in 100 µl) were incubated in the absence or in the presence of 32.1 µM of GlmR ([GlmR]/[GlmS] = 6) and 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5 and 1 mM of UDP-GlcNAc. The amount of CoASH produced was monitored at 412 nm by microplate reader at 37 °C and the specific activity of GlmS was calculated as indicated previously.