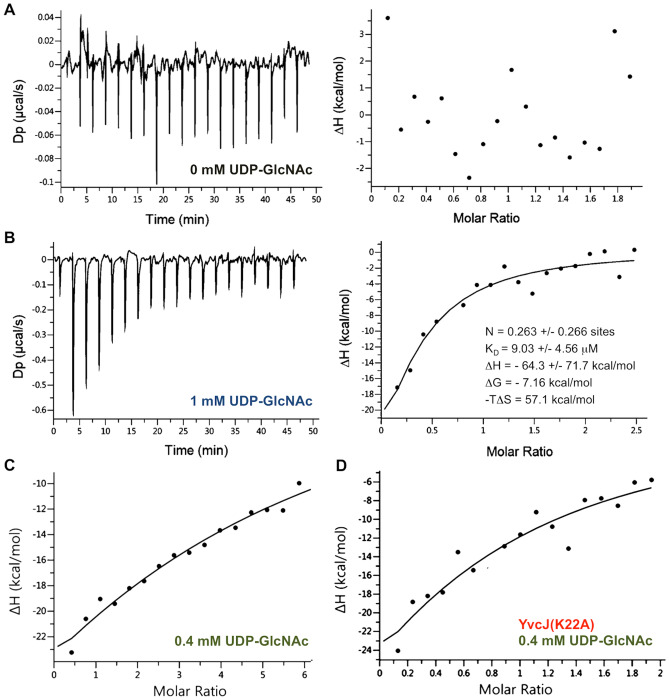
Figure 3.
Analysis of the interaction of GlmR with YvcJ by ITC. For all the experiments, the reference experiment with the titrant protein injected into the cell containing buffer 50 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.5, 50 mM NaCl and 5% glycerol and 0, 0.4 or 1 mM UDP-GlcNAc was subtracted from the experimental data before analysis. Each experiment was reproduced at least in triplicate. (A) YvcJ in the absence of UDP-GlcNAc. (B) YvcJ in the presence of 1 mM UDP-GlcNAc. For these two experiments, the titrant protein (in the syringe) is GlmR at a concentration of 210 µM; it is injected into the sample cell containing 16 µM of YvcJ. The left panel shows heat exchange upon ligand titration and right panel shows the corresponding integrated data with binding isotherms fitted to a single–site binding model. (C) YvcJ in the presence of 0.4 mM UDP-GlcNAc. The titrant YvcJ (88 µM) was injected into a cell containing 2.5 µM GlmR at 37 °C in the presence of 0.4 mM UDP-GlcNAc. (D) YvcJ(K22A) in the presence of 0.4 mM UDP-GlcNAc. The titrant YvcJ(K22A) (109 µM) was injected into a cell containing 10 µM GlmR at 37 °C in the presence of 0.4 mM UDP-GlcNAc. For these two experiments, only the integrated data with binding isotherms fitted to a single–site binding model are presented. However, the interaction between YvcJ (WT or K22A) and GlmR is too weak to determine the thermodynamic parameters and the KD in a reliable and accurate way.