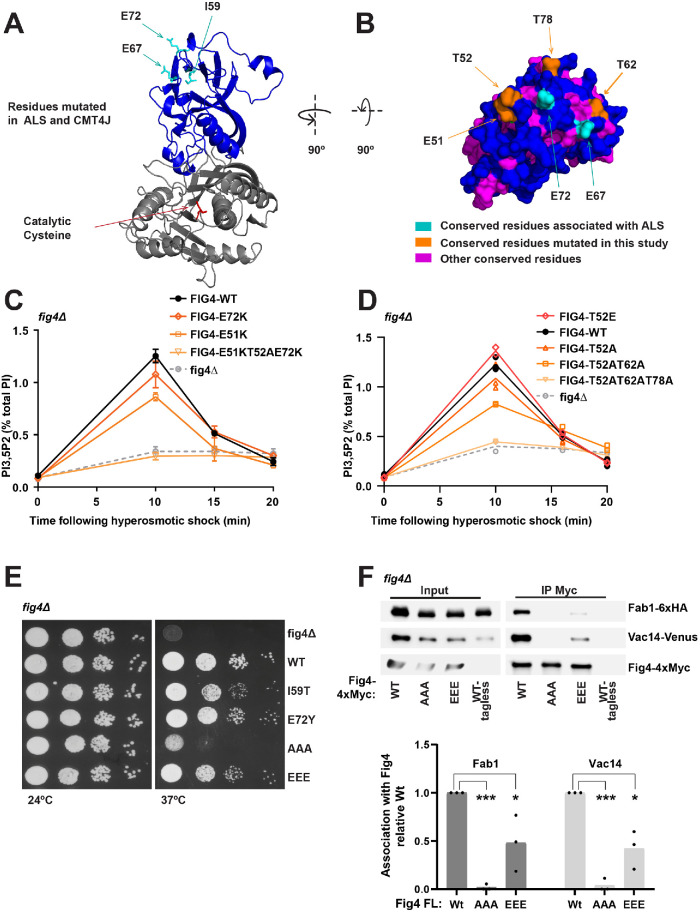
FIGURE 2:
A conserved N-terminal surface of Fig4 is required for the activation of Fab1 and for Fig4 binding to Fab1 and Vac14. (A, B) Predicted structure of the Fig4 phosphatase domain (amino acids 32–529) using Phyre2 (Kelley et al., 2015), based on homology with Sac1 (Manford et al., 2010). (A) Cartoon representation of the N-terminal lobe (blue) and catalytic region (gray) of the Fig4 phosphatase domain. ALS and CMT4J mutations (cyan) and the catalytic cysteine (red) are shown as sticks. I59 corresponds to human CMT4J mutation I41T. E67 and E72 correspond to ALS mutations D48G and D53Y, respectively. (B) Surface representation of a top-down view of the predicted Fig4 N-terminal surface. (C, D) PI3,5P2 was analyzed by HPLC from cells labeled with [3H]inositol. NaCl (0.9 M) was added to the media at 0 time. (C) Mean of three independent experiments. The 10 min level decreased relative to WT in E51K (p = 0.0008, two-tailed t test) and T52AE51KE72K (p = 0.0003, two-tailed t test). The change was not statistically significant for E72K (p = 0.0986, two-tailed t test). (D) Mean of two independent experiments with individual data points shown. (E) Growth defects in Fig4 mutants in fig4Δ Vac14-Venus Fab1-TAP at 37°C correlate with corresponding defects in elevation of PI3,5P2. Cells expressing no Fig4, Fig4-wild-type (WT), or indicated Fig4 mutants from a plasmid were grown on selective Sc–leu plates at 24° and 37°C. (F) Western blot of proteins immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody from a fig4Δ strain expressing Fig4-4xMyc from a plasmid with native 5′ and 3′ UTR, and Vac14-Venus and Fab1-6xHA expressed from their corresponding endogenous loci. Bar graph shows quantification of band densities in Western blot, relative to wild type, normalized to Fig4-Myc, with data points and mean from three independent experiments (* p < 0.01, *** p < 0.0001, by two-tailed t test). Fig4 mutants analyzed: E72K, E72Y, E51K, triple mutant T52AE51KE72K, T52E, T52A, double mutant T52AT62A, triple mutant T52ET62ET72E (EEE), and triple mutant T52AT62AT72A (AAA).