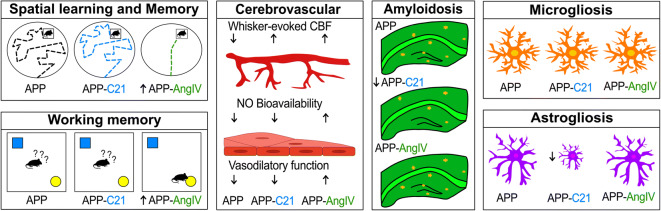
Fig. 9.
Schematic representation of AT2R and AT4R agonism on cognitive and cerebrovascular function, amyloidosis, and gliosis in APP J20 mice. AT2R agonism had no effect on spatial learning and memory, vasodilatory function, or nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability. AT2R agonism normalized neurovascular coupling, reduced dense core Aβ plaques, and reduced astrogliosis independent of persisting microgliosis. AT4R agonism rescued spatial learning and memory, vasodilatory function, NO bioavailability, and neurovascular coupling. AT4R agonism benefits were independent of persisting dense core Aβ plaque load, astrogliosis, and microgliosis. Overall, pharmacological manipulations of the RAS identify the AngIV/AT4R cascade as a promising target for AD intervention