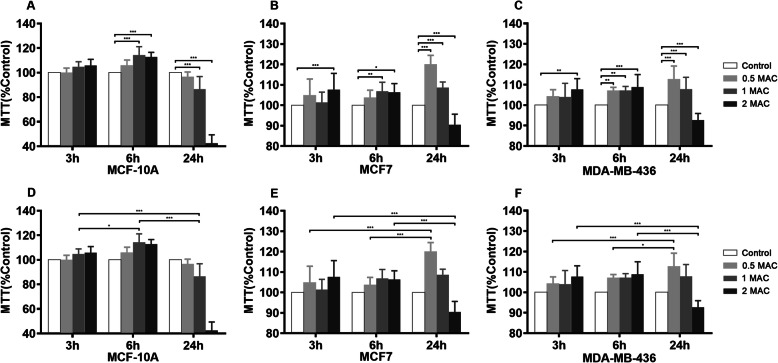
Fig. 1.
Sevoflurane modulates breast cancer cell survival in a dose- and time-dependent manner. a, b, c Dose-dependence relationships of sevoflurane exposure on breast cancer survival in vitro. d, e, f Time-dependence relationships of sevoflurane exposure on breast cancer cell survival in vitro. Exposure to sevoflurane at clinically relevant concentrations of 2 and 4% for 6 h significantly promoted breast cancer survival in normal breast cells (MCF10A) along with estrogen receptor-positive (MCF7) and estrogen receptor-negative (MDA-MB-436) breast adenocarcinoma cells. Treatment with 4% sevoflurane produced a statistically significant increase in cell survival after 3 h in both breast cancer cell types. Exposure to low-dose sevoflurane (1%) for an extended duration of 24 h also increased survival when compared to treatment for 3 and 6 h for the breast adenocarcinoma lines. Paradoxically, extreme exposure to 4% sevoflurane for 24 h reduced cell survival in all cell lines. All data are expressed as means ± SD from at least three separate experiments in duplicate or triplicate and analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey multiple comparison tests. * P < 0.5, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001