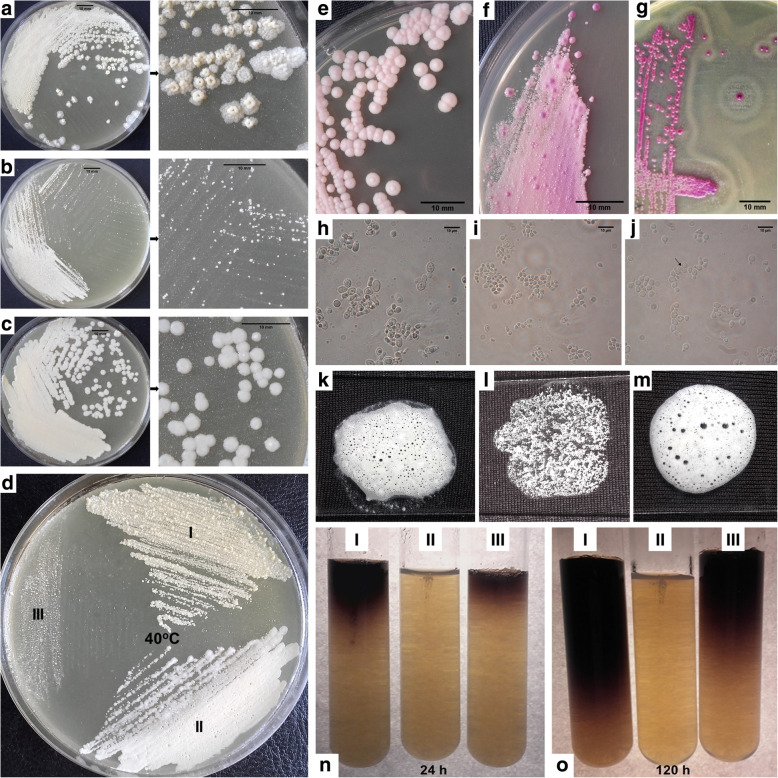
Fig. 4.
Species identification based on conventional mycological tests. a-c. Appearance of Malassezia species on MLNA medium after five days incubation at 32 °C, a. Malassezia furfur, b. Malassezia restricta, and c. Malassezia sympodialis; (d) differences in the ability to grow at 40 °C between isolated strains, I. Malassezia furfur, II. Malassezia sympodialis, and III. Malassezia restricta; (e-g) appearance of Malassezia species on CHROMagar Malassezia medium after four days of incubation at 32 °C, e. Malassezia furfur, f. Malassezia restricta, and g. Malassezia sympodialis; (h-j) micromorphology, typical for each species, observed with DIC microscopy, h. Malassezia furfur, i. Malassezia restricta, and j. Malassezia sympodialis, magnification: (h-j) 1000x; (k-m) differences in catalase activity between three isolated Malassezia strains. k. M. furfur, l. M. restricta, and M. M. sympodialis; (n, o) differences in β-glucosidase activity after 24 h (n) and 120 h (o) between three isolated Malassezia strains, I. M. sympodialis, II. M. restricta, and III. M. furfur. Scale bars correspond to: 10 mm in case of a, b, c, e, f, g and 10 μm in case of h, i, j