Fig. 5 |. Conformational changes of the bracelet domain and the thumb control movement of different RNA strands.
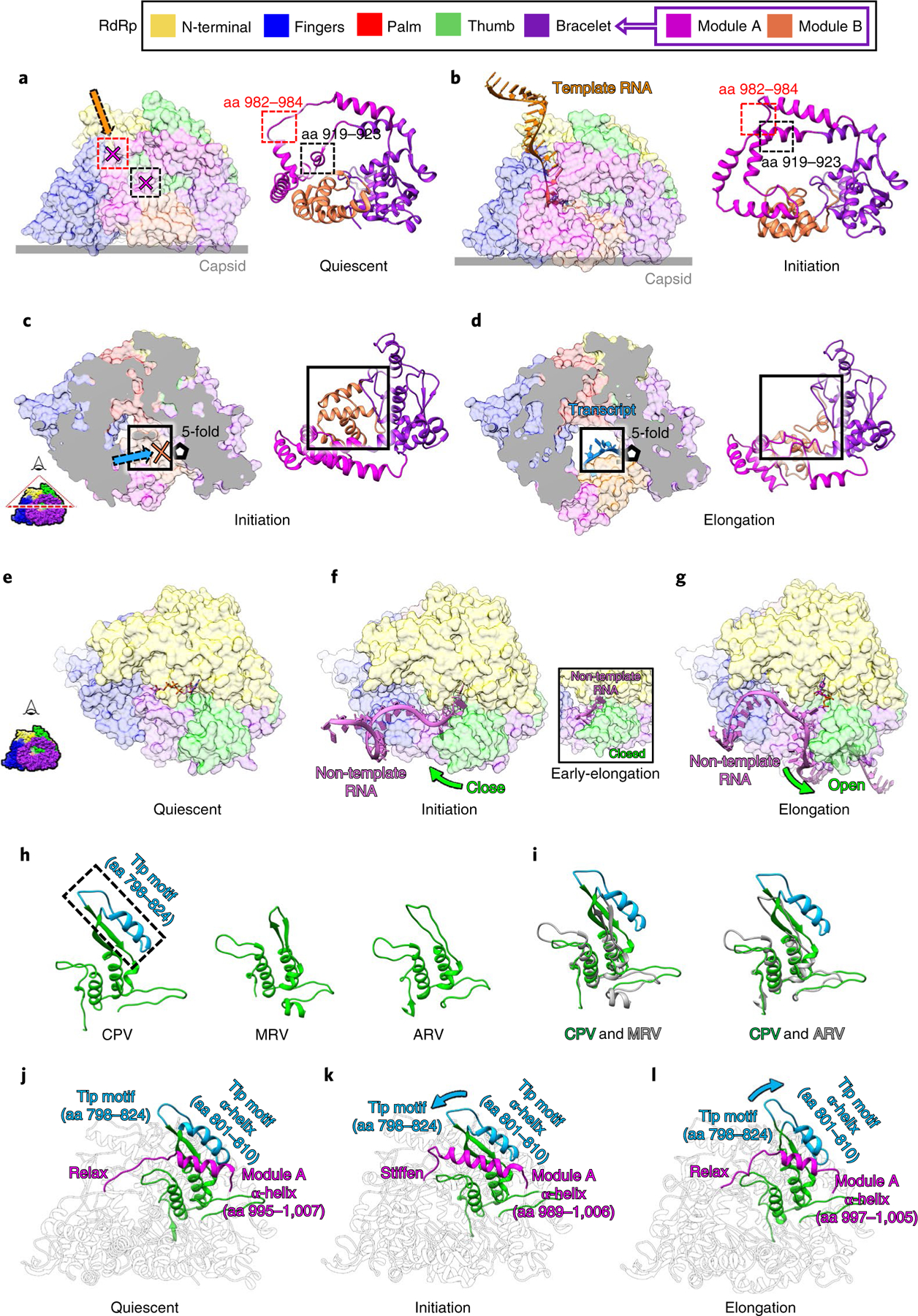
a,b, Conformational changes of module A regulate the template RNA entry tunnel and the polymerase active site. The template RNA entry tunnel and active site are blocked by module A of the bracelet domain in the quiescent state (a) and open in the initiation state when module A refolds (b). c,d, Conformational changes of module B regulate the transcript exit tunnel. The transcript exit tunnel is blocked by module B in the initiation state (c) and opens in the elongation state (d). e–g, Non-template RNA (ribbon) interacts with RdRp (surface representation) in the quiescent (e), initiation (f), early-elongation (inset) and elongation (g) states. h,i, Ribbon models of the thumb subdomains of CPV, mammalian reovirus (MRV), and aquareovirus (ARV) (h) and their superpositions (i), showing that only CPV has a tip motif. j–l, Ribbon models of RdRp in the quiescent (j), initiation (k) and elongation (l) states, highlighting in color the co-varying conformations of the tip motif of the thumb as it interacts with module A of the bracelet domain.
