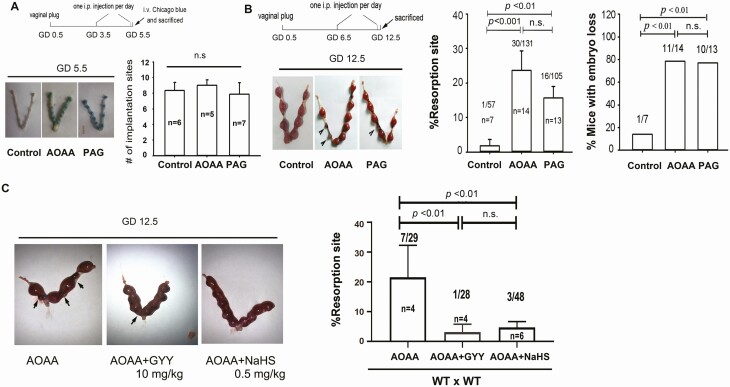
Figure 5.
Effect of H 2 S donors on pregnancy in wild-type mice receiving CBS and CSE inhibitors. (A) WT dams were treated with daily AOAA (50 mg/kg) or PAG (100 mg/kg) starting on gestational day (GD) 3.5; implantation sites on GD 5.5 were determined and averaged to be presented in the bar graph. n.s, not significant. (B) WT dams were treated with daily AOAA (50 mg/kg) or PAG (100 mg/kg) starting on GD 6.5. (C) WT dams were treated with daily AOAA (50 mg/kg) or PAG (100 mg/kg) starting on GD 6.5 for 6 days, followed by daily treatment with either GYY (10 mg/kg) or NaHS (0.5 mg/kg) starting on GD 6.5. Dams were killed on GD12.5 for examining the number of resorbed fetuses. Resorption rate and mice with embryo loss were then calculated as means ± SD and plotted. Black arrowheads denote the resorption sites. The numbers within bars indicate the number of pregnant mice, and the numbers above bars indicate the number of resorption events divided by the total number of implantation sites. AOAA, amino-oxyacetic acid; CBS, cystathionine β-synthase; CSE, cystathionine γ-lyase; GYY, GYY4137; H2S, hydrogen sulfide; n.s., not significant; PAG, propargylglycine; SD, standard deviation; WT, wild-type.