Figure 5.
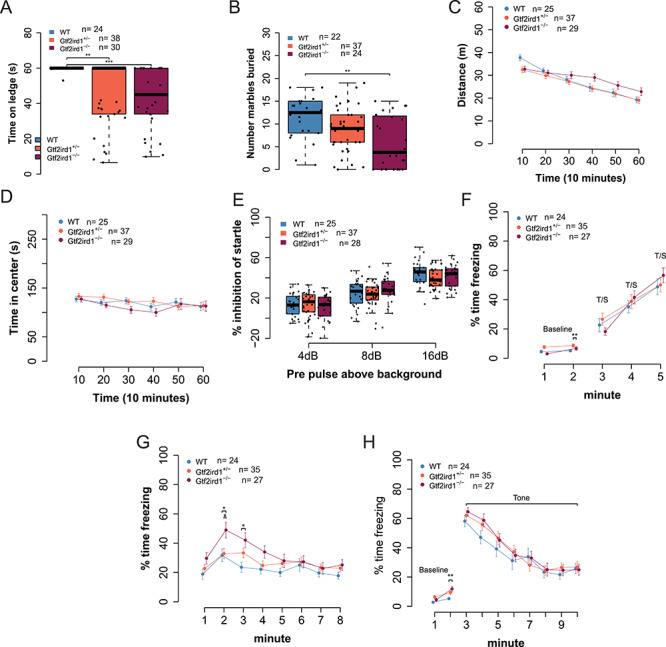
Homozygous frameshift mutation in Gtf2ird1 is sufficient to cause behavioral phenotypes. (A) Homozygous mutants have worse balance than WT littermates in ledge task. (B) Homozygous mutants bury fewer marbles than WT and heterozygous littermates. (C) Overall activity levels are not affected, but a time by genotype interaction shows the mutant animals are slower to habituate to the novel environment. (D) There is no difference in time spent in the center of the apparatus between genotypes. (E) All animals show an increase in startle inhibition when given a pre-pulse of increasing intensity. There is no difference between genotypes. (F) Acquisition phase of fear conditioning paradigm. All animals show the expected increase in freezing to additional foot shocks. (G) Gtf2ird1−/− animals show an early increased contextual fear memory response compared to WT and heterozygous littermates. (H) There were no significant differences between genotypes in cued fear. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
