Figure 7.
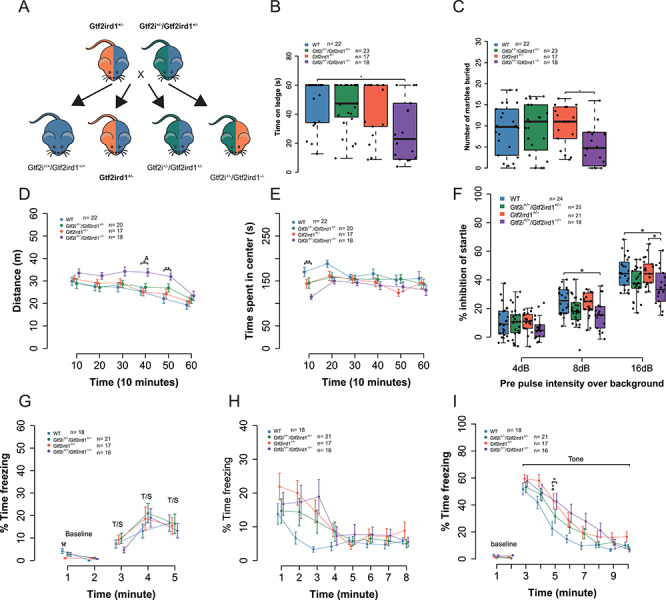
Gtf2i does not modify most of the phenotypes of Gtf2ird1 mutation. (A) Breeding scheme for behavior experiments. (B) The Gtf2i+/−/Gtf2ird1−/− animals fell off ledge sooner than WT littermates. (C) There was a main effect of genotype on marbles buried. Post hoc analysis showed that Gtf2i+/−/Gtf2ird1−/− buried fewer marbles than the Gtf2ird1−/− genotype. (D) Gtf2i+/−/Gtf2ird1−/− had increased overall activity levels in a 1-h activity task. (E) Gtf2i+/−/Gtf2ird1−/− showed a decreased time in the center of the apparatus compared to WT. (F) All animals show an increased startle inhibition when given a pre-pulse of increasing intensity. The Gtf2i+/−/Gtf2ird1−/− mutants show less of an inhibition at higher pre-pulse levels compared to WT and Gtf2ird1+/− animals. (G) All genotypes showed increased freezing with subsequent foot shocks. (H) All genotypes showed a similar contextual fear response. (I) There was a main effect of genotype on cued fear with the Gtf2ird1+/− and Gtf2i+/−/Gtf2ird1−/− genotypes showing an increased fear response compared to WT. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
