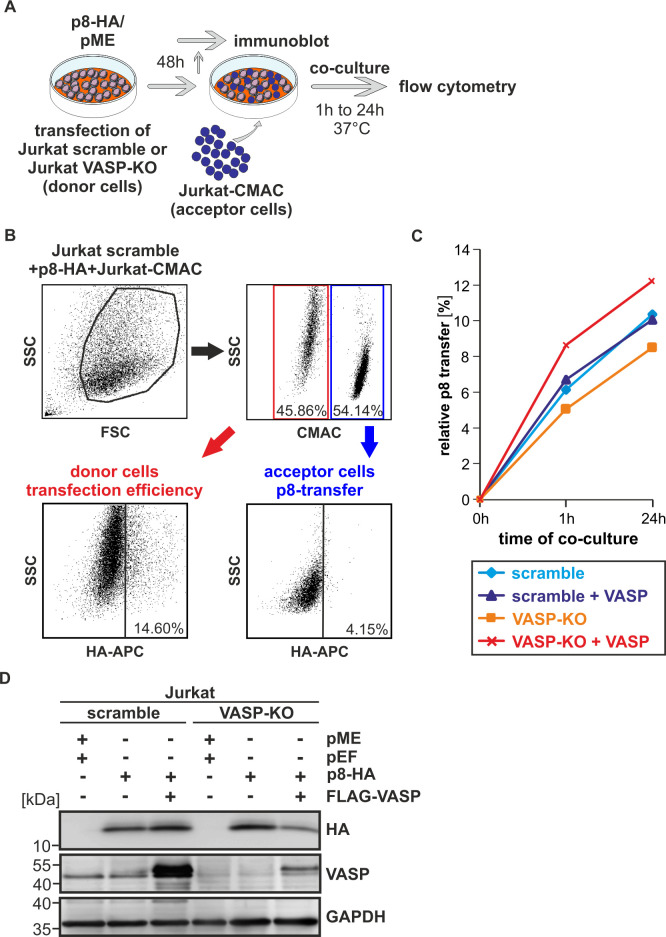
Fig 7. Knockout of VASP impairs p8-transfer between Jurkat T-cells.
(A) Experimental setup. (B-D) Stably transduced Jurkat T-cells (guide scramble, VASP-KO) were transfected with p8-HA expression plasmids or a control plasmid (pME) and FLAG-VASP or the respective control (pEF-1α). At 48 h post transfection, cells were either (B-C) co-cultured with pre-stained target Jurkat T-cells (Jurkat-CMAC; ratio 1:1, 37°C) for 0 h, 1 h, or 24 h and subjected to flow cytometry, or (D) cells were lysed for immunoblot analysis (B-C) Flow cytometry. At 48 h post transfection, equal amounts of donor and acceptor cells (1x106 cells each) were either directly fixed in 2% PFA and mixed (time point: 0 h), or they were co-cultured at 37°C for 1 h or 24 h before fixation. After intracellular staining using HA-specific, APC-labeled antibodies or the respective isotype-matched control antibodies, flow cytometry was performed. (B) Representative dot plots at 1 h post co-culture are shown. Upper left: Dot plots display the forward scatter (FSC) plotted against the side scatter (SSC) and living cells are gated (black gate). Upper right: CMAC-specific fluorescence is plotted against the SSC, which allows discrimination between CMAC-negative donor (red gate) and CMAC-positive acceptor (blue gate) cells. Lower plots: HA-specific fluorescence is plotted against the SSC and numbers represent the efficiency of transfection within the CMAC-negative donor cells (lower left) or the transfer of p8 within the CMAC-positive acceptor cells (lower right). (C) The relative transfer of p8 between p8-expressing CMAC-negative Jurkat donor cells (scramble, scramble and FLAG-VASP, VASP-KO, VASP-KO and FLAG-VASP) and CMAC-positive Jurkat acceptor cells is shown over time (0 h, 1 h, 24 h). The means of at least three independent experiments are shown. (D) Western blot analysis depicting p8-HA and VASP in stably transduced Jurkat T-cells (scramble, VASP-KO).