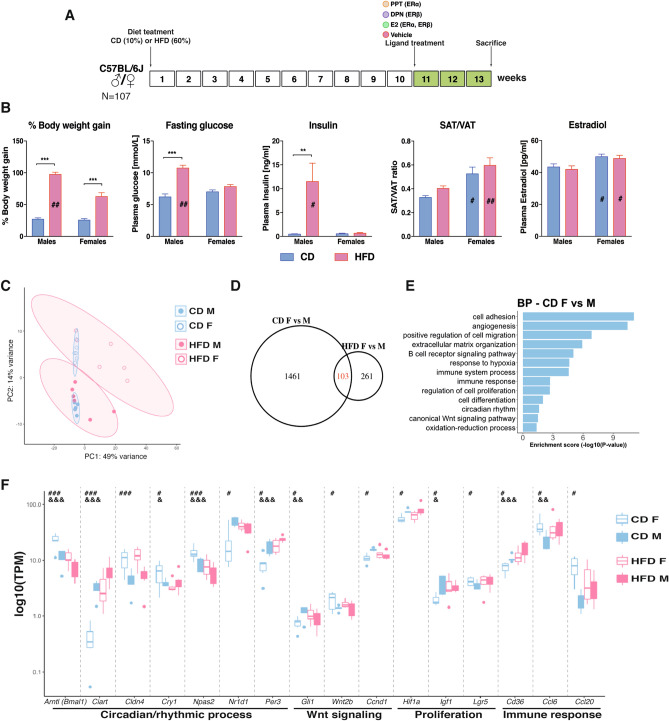
Figure 1.
The male metabolic profile is more sensitive to HFD and the colon trancriptome exhibits sex differences independent of diet. (A) Experimental study design. Mice of both sexes were given CD or HFD for 13 weeks and injected with different estrogenic ligands or vehicle for the last 3 weeks prior to sacrifice. (B) Percentage of BW gain, fasting glucose level, insulin level, SAT/VAT ratio, and plasma estradiol levels. (C) Principal component analysis of RNA-seq samples for male (unfilled) and female (filled) mice fed a CD (blue) or HFD (red) (n = 5–6). (D) Venn diagram comparing differentially expressed genes in colon between male and female mice fed a CD or a HFD. Genes were considered as differentially expressed when p value < 0.05 and log2FC > |0.4|. (E) Biological process enrichment analysis based on genes differentially expressed between the sexes during CD. (F) Boxplot of TPM values of genes differentially expressed between sexes and/or dietary conditions. The results are presented as mean ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA followed by fisher's LSD test, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. # indicate significant sex differences during CD, ## during HFD and ### during both dietary conditions; & indicate significantly difference between CD and HFD in females, && in males, and &&& in both sexes. Blue color indicates CD and pink HFD.