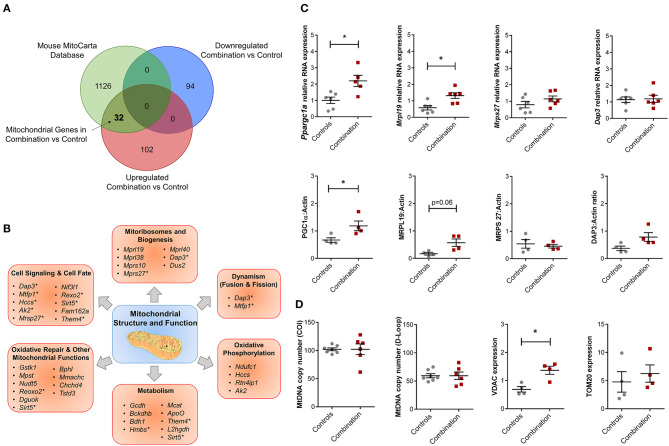
Figure 5.
Combination exposed offspring hearts enriches discrete classes of mitochondrial genes. Genes that were duplicated or non-annotated were excluded, resulting in 228 differentially expressed genes (DEG) with 94 down and 134 upregulated in combination exposed hearts when compared to controls. (A) The 228 DEGs were plotted in a Venn diagram against 1,158 mitochondrial associated genes (MitoCarta Database, Mouse) and depicted 32 upregulated mitochondrial genes (Table S9) with none downregulated in the combination exposed offspring hearts. (B) Mitochondrial functions associated with the 32 upregulated mitochondrial genes were: cell signaling and cell fate, mitochondrial biogenesis, dynamism, oxidative phosphorylation, metabolism, oxidative repair and other mitochondrial functions. *Genes with multiple functions; shown in more than one category. (C) RNA expression of Ppargc1a and Mrpl19 were significantly upregulated with fold change (FC) of 2.24 and 2.28, respectively (p < 0.05) in combination exposed newborn hearts (red squares) compared to controls (gray circles; n = 6/group). We showed no significant change in RNA expression of Mrps27 (FC = 1.09, p = 0.6) or Dap3 (FC = 1.10, p = 0.75). Consistent with the RNA expression, protein expression of PGC1α was significantly increased in newborn hearts exposed to diabetes and HF diet when compared to controls (n = 4/group, p < 0.05). We observed a non-significant upregulation trend for MRPL19 and DAP3 protein expressions with no change in MRPS27. (D) Relative mtDNA copy number was not different by mtDNA expression of either cytochrome-c oxidase I (COI) or mitochondrial control region (D-loop). However, combination exposed hearts had higher protein expression of Voltage dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC) and a trend toward higher Translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 20 (TOM20).