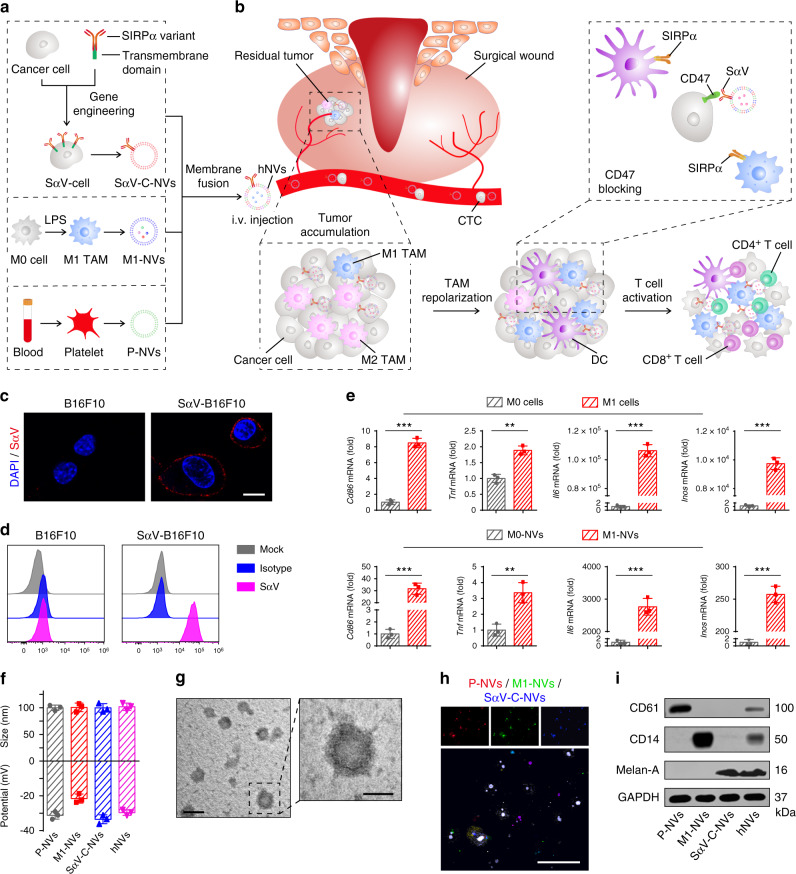
Fig. 1. Schematic and characterization of hNVs.
a Schematic showing the hNVs consist of engineered SαV-C-NVs, M1-NVs, and P-NVs. b Schematic showing the hNVs efficiently interact with CTCs in the blood, accumulate in the post-surgical tumor bed, repolarize TAMs towards M1 phenotype, and block the CD47-SIRPα ‘don’t eat me’ pathway, thus promoting macrophage phagocytosis of cancer cells, as well as boosting antitumor Tcell immunity. c, d Immunofluorescence imaging c and flow cytometry analysis d of SαV expression on original and engineered B16F10 cells. Scale bar, 10 µm. e Relative mRNA expression of Cd86, Tnf, Il6, and Inos in M0 cells, M1 cells, M0-NVs and M1-NVs. f Hydrodynamic size and zeta potential of P-NVs, M1-NVs, SαV-C-NVs, and hNVs measured by DLS. g TEM images of hNVs. Scale bar, 100 nm and 50 nm in the left and right panel, respectively. The samples were negatively stained with uranyl acetate. h Immunofluorescence images of hNVs. Scale bar, 10 µm. i Western blot analysis of specific protein CD61, CD14, and Melan-A in the samples of P-NVs, M1-NVs, SαV-C-NVs, and hNVs. All data are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). Statistical significance was calculated via unpaired two-tailed t test. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.