Fig. 3.
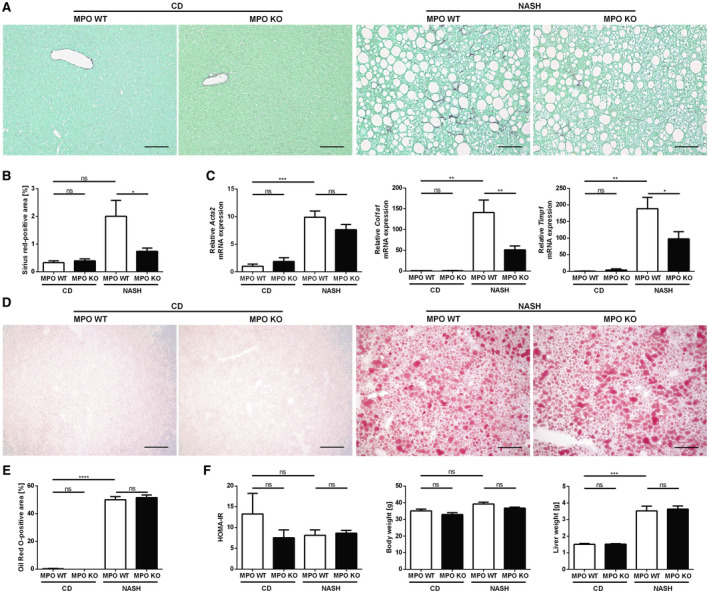
MPO deficiency attenuates liver fibrosis in a dietary mouse model of NASH. Hepatic fibrosis, steatosis, and metabolic parameters were evaluated in MPO KO and WT littermates that were fed chow diet (“CD”) or HFCholC diet (“NASH”) for 24 weeks (nMPO WT CD = 3‐4; nMPO KO CD = 6; nMPO WT NASH = 13‐14; nMPO KO NASH = 16‐17). Liver fibrosis was quantified by sirius red staining (A) (scale bar: 100 µm), quantification of stained area (B), and qPCR (C) of fibrosis‐related genes. (D) Oil Red O staining was used to evaluate hepatic steatosis (scale bar: 200 µm). (E) Quantification of the staining. (F) HOMA‐IR, body weight, and liver weight. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001. Abbreviations: Acta2, α‐smooth muscle actin; Col1a1, α1 type I collagen; Timp1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1.
