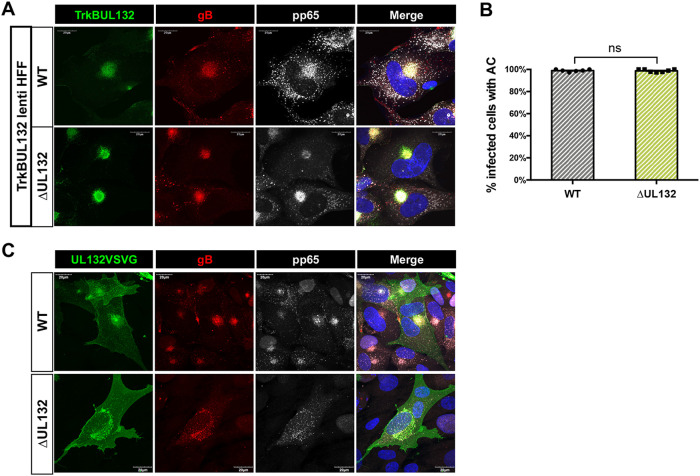
FIG 7.
The cytoplasmic domain of UL132 is sufficient to rescue AC formation during ΔUL132 HCMV infection. (A and B) TrkBUL132-expressing cells rescued AC formation following ΔUL132 virus infection. Confluent TrkBUL132 (Myc-tagged)-expressing cells were infected with WT or ΔUL132 HCMV at an MOI of 3. At 4 dpi, infected cells were harvested and processed for immunofluorescence to detect the expression of the Myc, gB, or pp65. (A) TrkBUL132-expressing cells rescued AC formation following ΔUL132 HCMV infection. Representative images are shown (magnification, ×120). (B) Quantification of AC formation percentages in HCMV-infected TrkBUL132-expressing HFF cells. Random fields with 70 to 95 cells per field were counted and quantified. Error bars denote SEM. Significance was determined using the Student t test (ns, not significant). The experiments were repeated twice, and the data shown are from one experiment. (C) Transiently expressed UL132VSVG cannot rescue AC formation in ΔUL132 HCMV-infected HFFs. A UL132VSVG (HA tag)-expressing vector was electroporated into HFFs, and HFFs were then infected with WT or ΔUL132 HCMV at an MOI of 2. Coverslips were collected, fixed, and analyzed using immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy. Representative images from two independent experiments are shown.