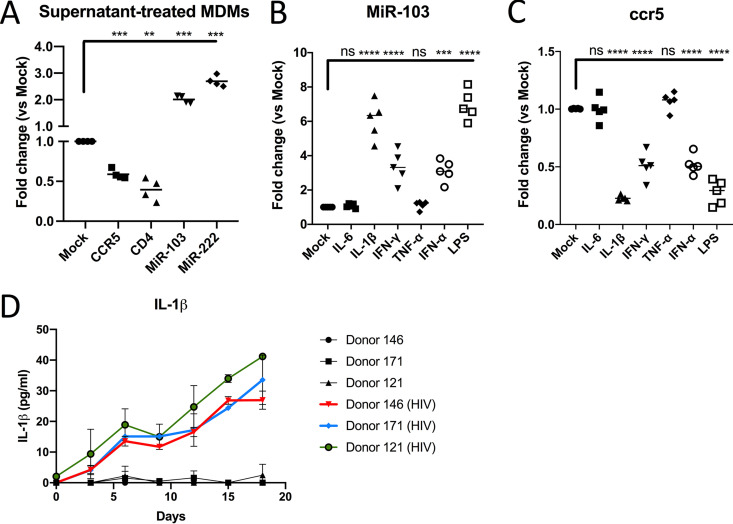
FIG 4.
Macrophage activation by IL-1β reduces CCR5 expression and enhances miR-103 (see also Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). (A) Virus-cleared supernatants from infected macrophages were added to new MDM cultures (n = 4 blood donors; Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test) for 48 h, and the levels of CCR5 mRNA, CD4 mRNA, miR-103, and miR-222 were determined by real-time qPCR. Bars represent the mean fold changes compared to mock (untreated) cells. (B) MDMs derived from different blood donors (n = 5; Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test) were treated with the indicated MDM activators for 48 h, and miR-103 expression was measured by real-time qPCR. Bars represent the mean fold changes compared to mock (untreated) cells. (C) CCR5 mRNA levels were measured by real-time qPCR in the same samples as the ones described above for panel B. Bars represent the mean fold changes compared to mock (untreated) cells. (D) MDMs from 3 blood donors were infected with HIV-1, and the levels of IL-1β released into the supernatants were compared to that of uninfected cells at the indicated time points by an ELISA. Shown are picograms per milliliter ± SD of IL-1β.