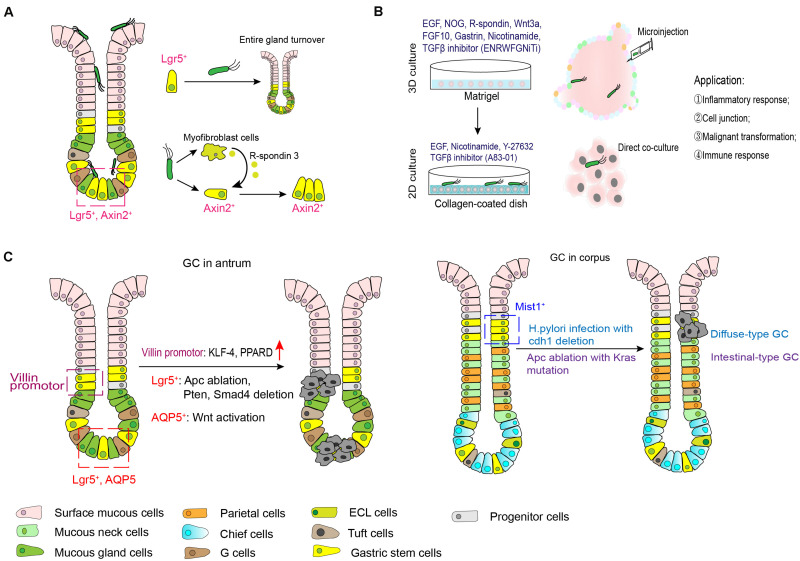
FIGURE 4.
Role of gastric stem cells in H. pylori infection and gastric carcinogenesis. (A) H. pylori can colonize in gastric surface cells, neck regions and even the base of antral glands. Gland-colonized bacteria directly or indirectly expands the stem cell pools. (B) Microinjection of H. pylori with gastric organoid can mimic the model of H. pylori infection in vitro, while co-culture model of H. pylori and organoid-derived primary gastric epithelial cells are more easier to investigate the pathogenesis of this bacterium. (C) The candidate stem cell origin and possible mechanism behind gastric oncogenesis.