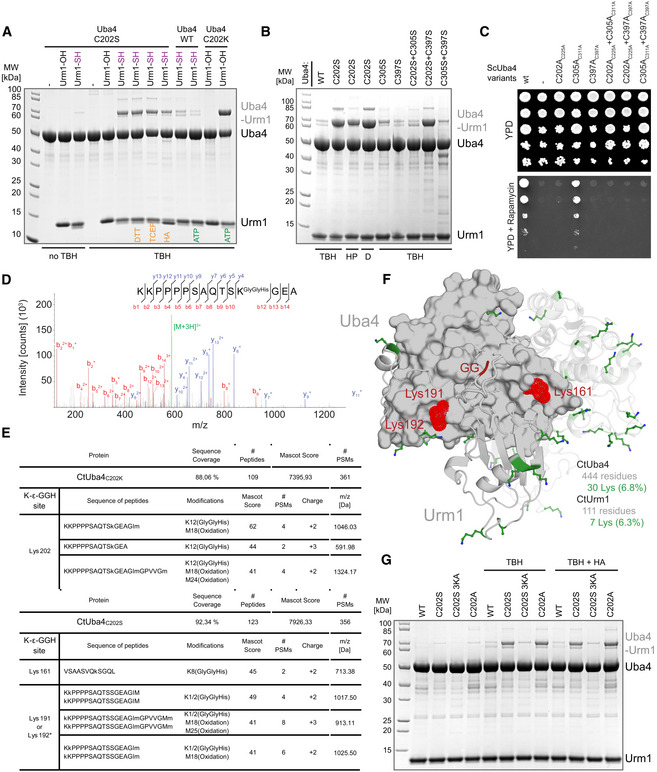
Analysis of covalent adduct formation between CtUba4 WT or C202 mutants and carboxylated (–OH) or thiocarboxylated (–SH) CtUrm1 in the presence or absence of TBH, DTT, TCEP, and HA, respectively. ATP: Adenosine triphosphate TBH: tert‐Butyl hydroperoxide HA: Hydroxylamine; DTT: 1,4‐Dithiothreitol; TCEP: Tris(2‐carboxyethyl)phosphine.
Analysis of covalent adduct formation between CtUba4 WT/cysteine mutants and CtUrm1‐COSH in the presence of oxidizing agents. HP: Hydrogen peroxide; D: Diamide.
Phenotypic analysis of ScUba4 mutant yeast strains in response to rapamycin.
MS/MS spectrum of the K202‐ε‐GGH containing peptide from CtUba4C202K. A representative annotated fragmentation spectrum is shown with the b‐ and y‐ions marked in red and blue, respectively. The precursor ion at m/z 591,98 is labeled in green. The peptide sequence is shown at the top with the collision‐induced fragmentation pattern. The Urm1 conjugation site was identified by detection of the GGH remnant motif generated by chymotryptic digestion.
The table shows parameters of mass spectrometry identification of CtUba4C202K and CtUba4C202S with lists of detected peptides containing the K‐ε‐GGH remnant motif of Urm1. In CtUba4C202K, the conjugation site on K202 was confirmed. In the TBH treated samples of CtUba4C202S, several potential conjugation sites were found. We present only high confidence peptides reaching a Mascot score higher than 40, which were detected in all analyzed samples. Asterisks indicate ambiguous site localization of K‐ε‐GGH. #PSMs: number of peptide‐to-spectrum matches; m/z: mass‐to-charge ratio of precursor ion.
Localization of all lysine residues (shown as green sticks) on the structure of CtUba4C202K‐Urm1. CtUrm1 C‐terminus and the lysine residues of CtUba4C202S that become covalently linked to Urm1‐COSH in oxidizing conditions are presented in red.
Analysis of covalent adduct formation between CtUba4 WT or Cys202 mutants and thiocarboxylated (–SH) CtUrm1 in the presence or absence of TBH and HA, respectively.