Figure 5.
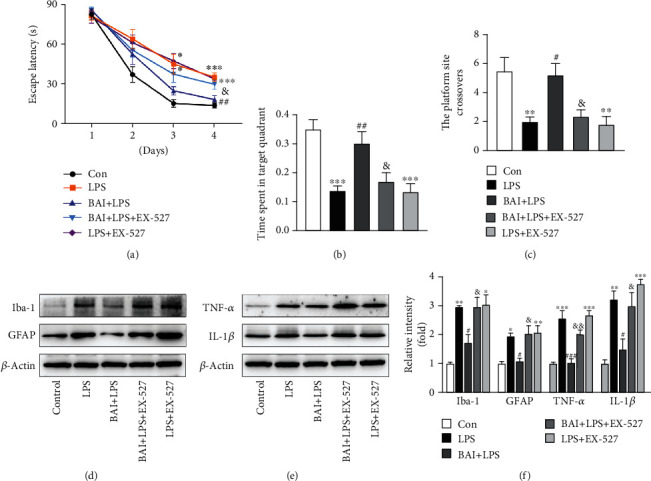
BAI-improved neuroinflammation and neurocognitive impairment induced by exposure to LPS in mice are SIRT1 dependent. Mice were divided into five groups: control, LPS, BAI+LPS, BAI+LPS+EX-527, and LPS+EX-527. (a) Latency to the platform during spatial working memory testing. (b) Time spent in the target quadrant during probe testing. (c) Platform-site crossings during the probe trial. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 8–10). (d) Western blot analysis of Iba-1 and GFAP in the hippocampus following LPS and BAI treatment, with or without EX-527 treatment. (e) Immunoblots of the inflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and TNF-α. (f) Quantification of the data shown in d and e. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 5/group). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, control vs. LPS or LPS+EX-527; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, BAI+LPS vs. LPS; &P < 0.05, &&P < 0.01, BAI+LPS vs. BAI+LPS+EX-527. EX-527, a specific SIRT1 inhibitor.
