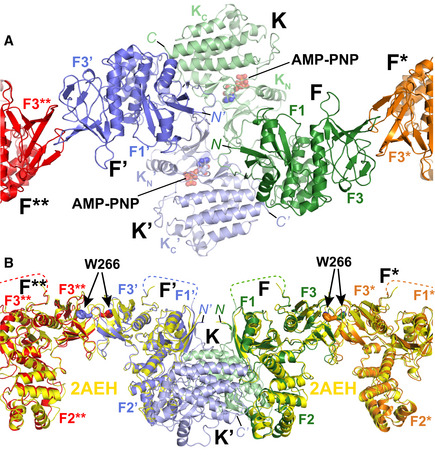
Close‐up of the central symmetric dimer of the AMP‐PNP particle from the membrane distal view. Interfaces within the symmetric dimer are formed intramolecularly between the FERM and kinase domains (F and K; F’ and K’). Intermolecular interfaces are formed within the symmetric dimer between F and K’, F’ and K as well as K and K’. Intermolecular interactions that link symmetric dimers are formed between two FERM domains (F and F*; F’ and F**). Coloring is as in Fig
1E. The FERM subdomains F1 and F3 (F2 is not visible from this view), kinase N‐ and C‐lobes (K
N, K
C), AMP‐PNP and the N‐ and C‐termini (N, C) are labeled.